Reeve - Developer Guide
Reeve - Developer Guide
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. About
- 3. Understanding the guide
- 4. Getting started
- 5. Design
- 6. Implementation
- 7. Documentation
- 8. Logging
- 9. Testing
- 10. Configuration
- 11. DevOps
- Appendix A: Product Scope
- Appendix B: User Stories
- Appendix C: Use Cases
- Appendix D: Non-Functional Requirements
- Appendix E: Glossary
- Appendix F: Instructions for Manual Testing
1. Introduction
Welcome to Reeve!
Reeve is a desktop application for private tutors to better manage both administrative and academic details of their students, optimised for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) for receiving inputs while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for displaying information. In addition, Reeve comes with a customisable personal scheduler to assist users to keep track of their classes. Reeve also allows users to set timely reminders for themselves.
Reeve is optimized for users that are very comfortable with typing as it works on a Command Line Interface (CLI).
Students’ details are displayed in a neat and organized manner through the use of a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
2. About
This developer guide will provide you the details of the software architecture and implementation of Reeve. It is made for developers who wish to understand the internal and external workings of the application.
All developers are warmly welcome to contribute your ideas and improve Reeve! To contribute, simply head over to our github and raise an issue.
3. Understanding the Guide
This section will share with you how should you go about understanding this guide in order to best understand Reeve.
We have adopted the “top-down” approach into the structure of this guide where we will first look at the high-level structure of our application before going into the implementation details of each feature.
We highly encourage you to read the guide from top to bottom in order to have the best understanding of Reeve.
Here is a summary (Table 1) of the symbols that are used in this Developer Guide:
Table 1: Summary of symbols
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
code |
Code snippets |
| Important information | |
| Tips |
4. Getting Started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
5. Design
5.1 Architecture
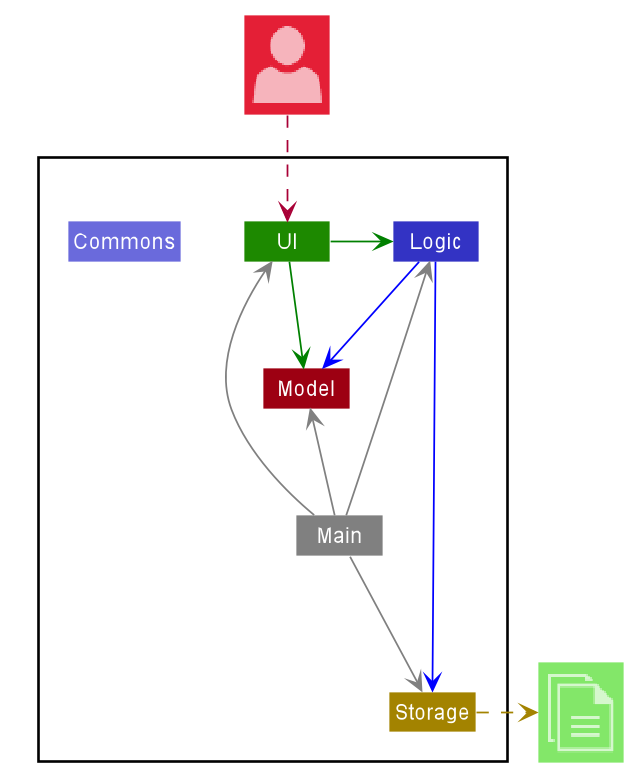
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App. Given below is a quick overview of each component.
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Main has two classes called Main and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Each of the four components,
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - exposes its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which implements the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the Logic component (in the diagram below) defines its API in the Logic.java interface and exposes its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which implements the Logic interface.
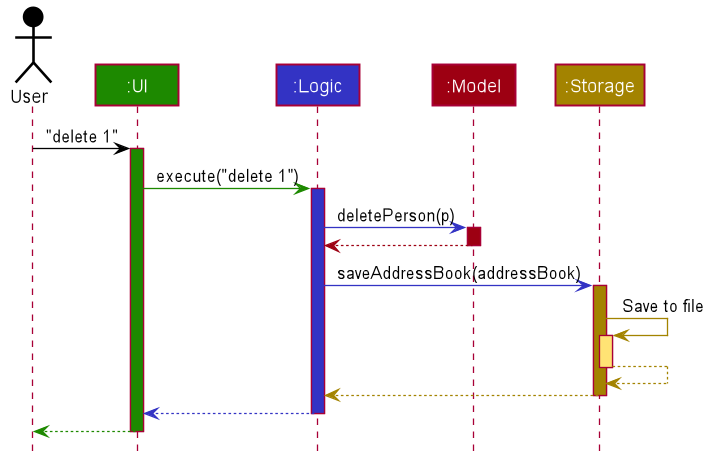
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
The sections below give more details of each component.
5.2 UI component
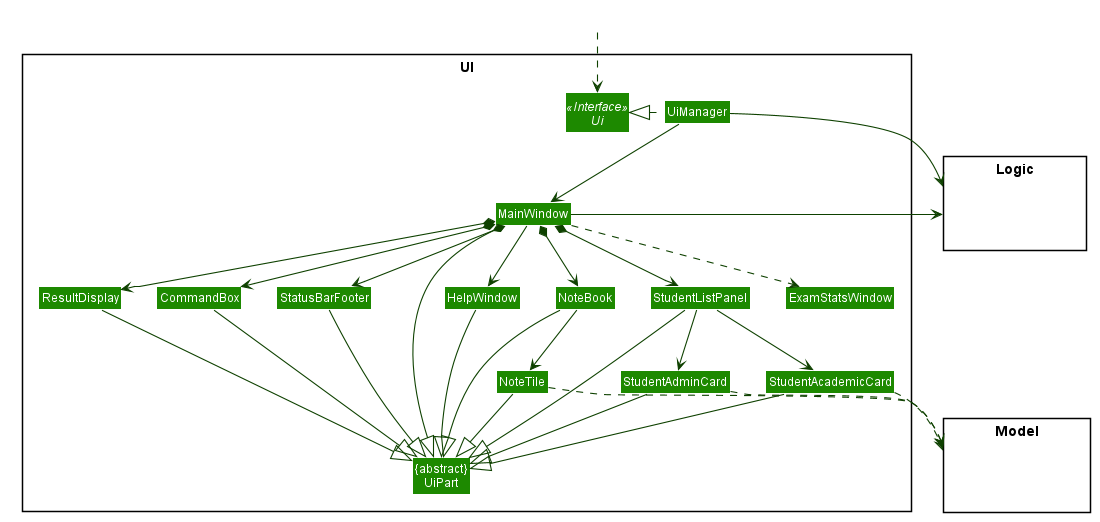
API :
Ui.java
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, StudentListPanel, Notebook etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class.
The UI component uses JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- Executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - Listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data.
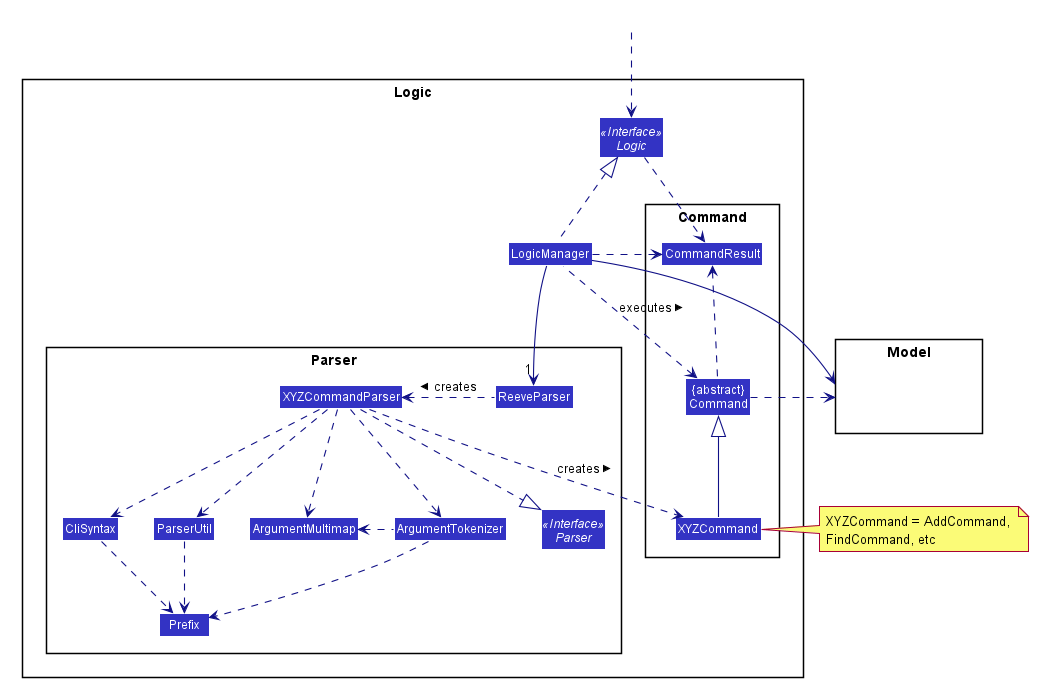
5.3 Logic component

API :
Logic.java
-
Logicuses theReeveParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
Commandobject which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command execution can affect the
Model(e.g. adding a student). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is passed back to theUi. - In addition, the
CommandResultobject can also instruct theUito perform certain actions, such as displaying help to the user.
Given below is the Sequence Diagram for interactions within the Logic component for the execute("delete 1") API call.
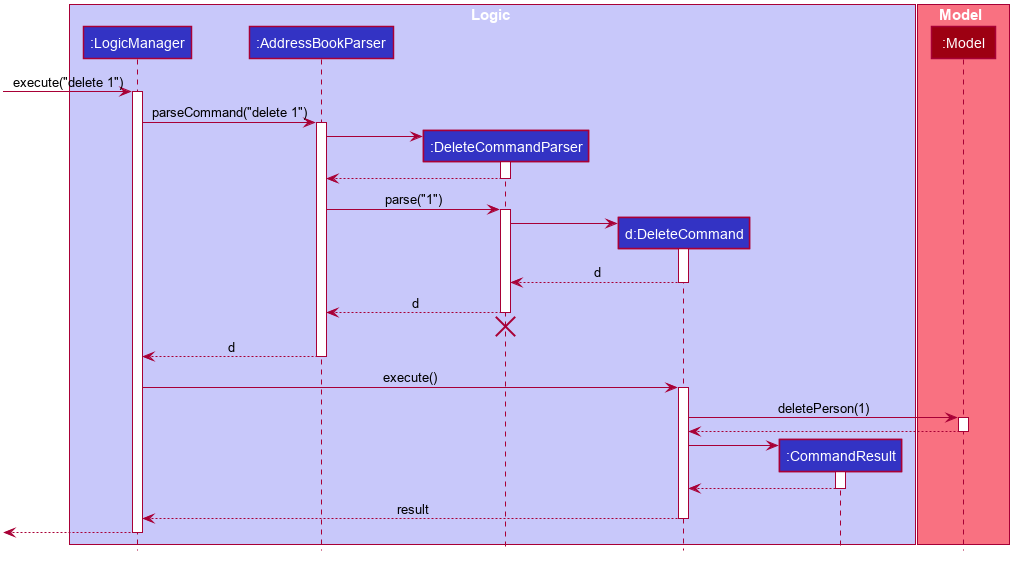
DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
5.4 Model component
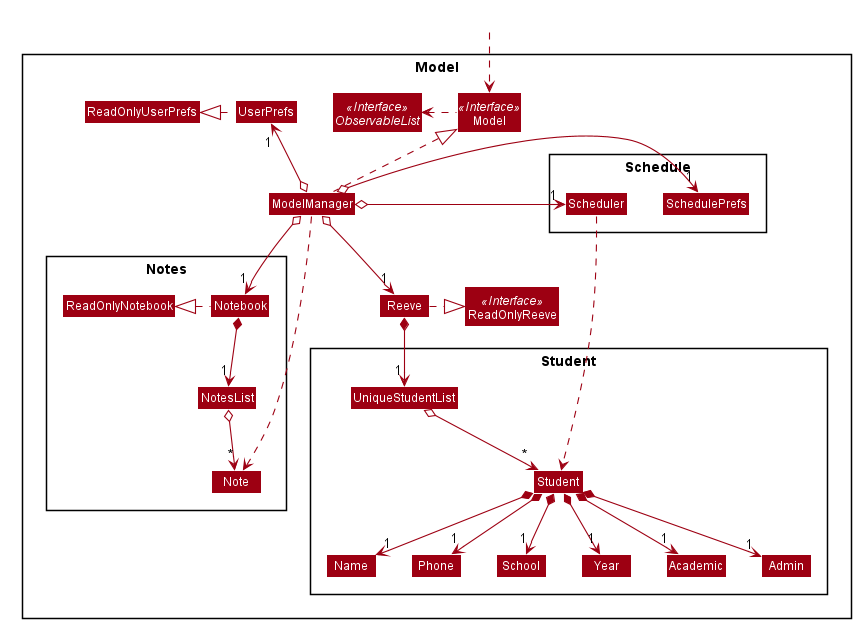
API : Model.java
The Model,
- stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. - holds the data of Reeve in memory.
- exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Student>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - does not depend on any of the other three components.
5.5 Storage component
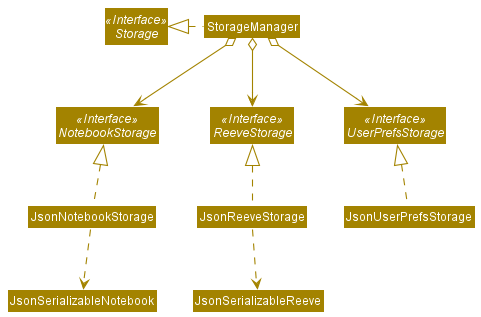
API : Storage.java
From the diagram above, the Storage component,
- can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. - can save
Reevedata in json format and read it back. - stores
StudentandNotedata from theModelcomponent inJsonSerializableReeveandJsonSerializableNotebookobjects respectively.
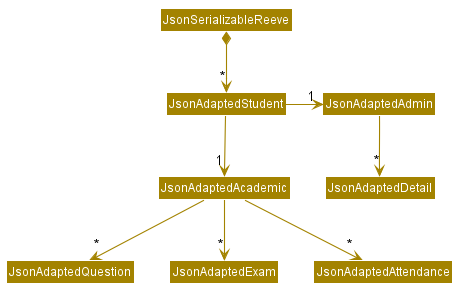
The JsonSerializableReeve component stores JsonAdaptedStudent objects converted from the Student objects in the Model component.
Each JsonAdaptedStudent object also contains json-friendly versions of Student data as shown in the class diagram below.
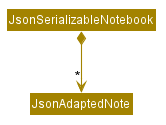
The JsonSerializableNotebook component stores JsonAdaptedNote objects converted from Note objects in the Model component, as shown in the class diagram below.
5.6 Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
6. Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
6.1 General features
This section describes some key details on how general features are implemented.
6.1.1 Help Command
The following describes the flow of how HelpCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input, the
HelpCommand#execute(Model model)is called. - A
CommandResultwith theshouldShowHelpfield set to true is returned andMainWindow#handleHelp()is called. - A Help display window will be opened showing a link to the User Guide.
![]() If there is already a Help window already opened, and
If there is already a Help window already opened, and HelpCommand is executed, HelpWindow#focus() will be called to focus on the already opened window.
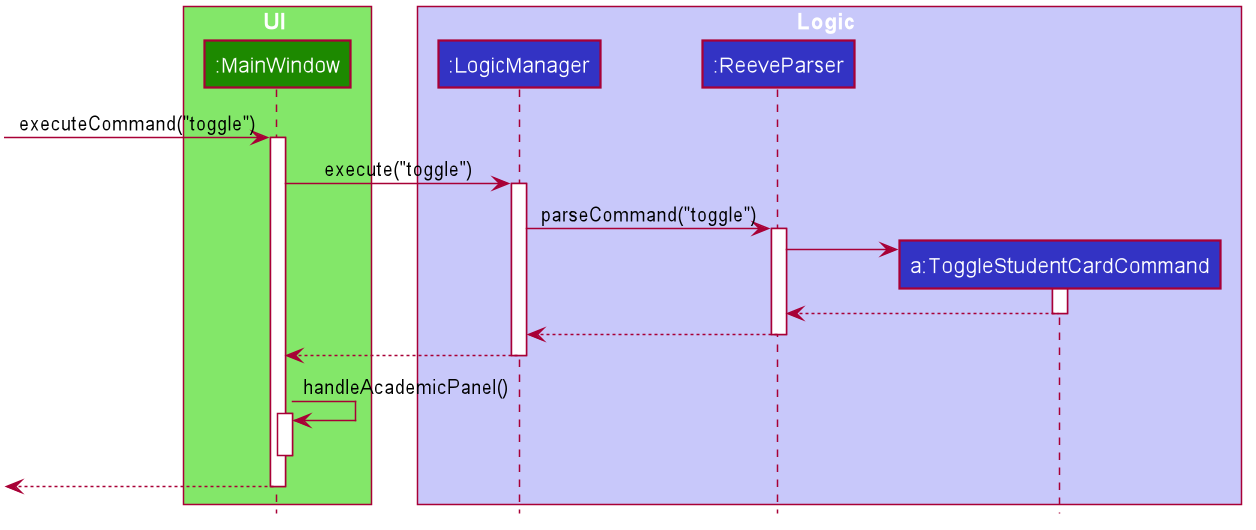
6.1.2 Toggle Command
The following describes the flow of how ToggleStudentCardCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input, the
ToggleStudentCardCommand#execute(Model model)is called. - A
CommandResultwith thetoggleStudentCardfield set to true is returned andMainWindow#handleAcademicPanel()is called. - Student cards in
StudentListPanelwill be switched.
![]() By default,
By default, StudentListPanel uses the StudentAcademicCard.
The following sequence diagram shows how the ToggleStudentCardCommand execution works.
The following explains the design considerations of the toggle command.
Aspect: How the GUI responds when toggle is executed
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Switch between two types of student cards, student academic card and student admin card for the cards used in the student list panel.
- Pros: Easy to implement, reduces cluttering of information, allows for better focus on different information,.
- Cons: Can take a long time to execute finish or introduce unfinished toggling if student list is large.
-
Alternative 2: Introduce two tabs, one for admin details and the other for academic details and toggling switches between these two tabs.
- Pros: Student list size does not slow down execution of command.
- Cons: Double the work when executing commands such as
findbecause there are now two lists to update, repeat of basic information such as student’s name, phone, school and academic level, harder to implement.
6.1.3 Exit Command
The following describes the flow of how ExitCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input, the
ExitCommand#execute(Model model)is called. - A
CommandResultwith theshouldExitfield set to true is returned andMainWindow#handleExit()is called. - Reeve shuts down.
6.2 Student administrative details features
This section describes some key details on how administrative details features are implemented.
6.2.1 Add Student Command
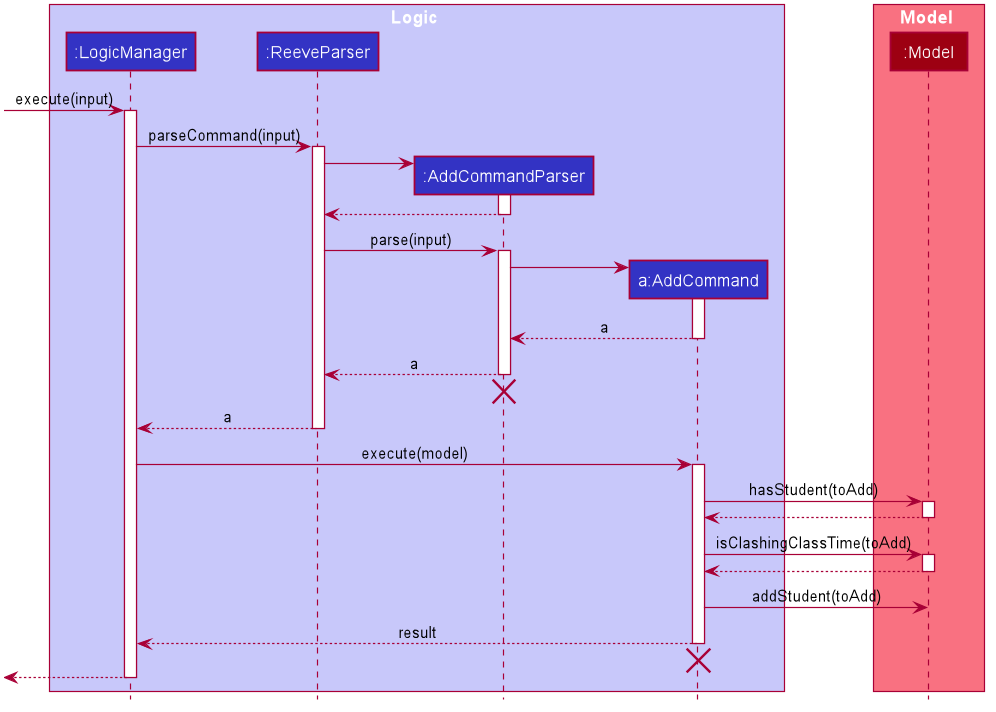
The following describes the flow of how AddCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input, the
AddCommand#execute(Model model)is called which checks whether the added student already exists in theUniqueStudentListusing theModel#hasStudent(Student toAdd). - A unique student is defined by
Name,Phone,SchoolandYear. If a duplicate student is defined, aCommandExceptionis thrown and the student will not be added. - The
AddCommand#execute(Model model)also checks if the student to be added has clashingClassTimewith other students already in theUniqueStudentList. - Two student’s
ClassTimeare considered clashing if they overlap either partially or fully. ACommandExceptionwill be thrown if there are other students with clashing class time. - If the added student is not a duplicate and there are no clashes in class time, then the
Model#addStudent(Student toAdd)is called to add the student. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message and the added student. - The student is be added into
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram summarizes the execution of the AddCommand:
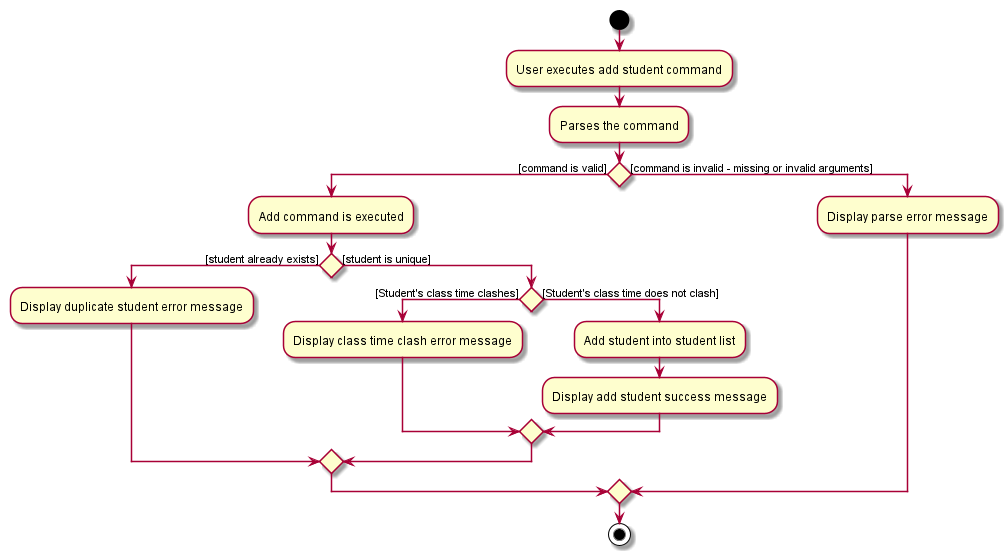
The following activity diagram summarizes the flow of events when the AddCommand is being executed:
6.2.2 Edit Student Command
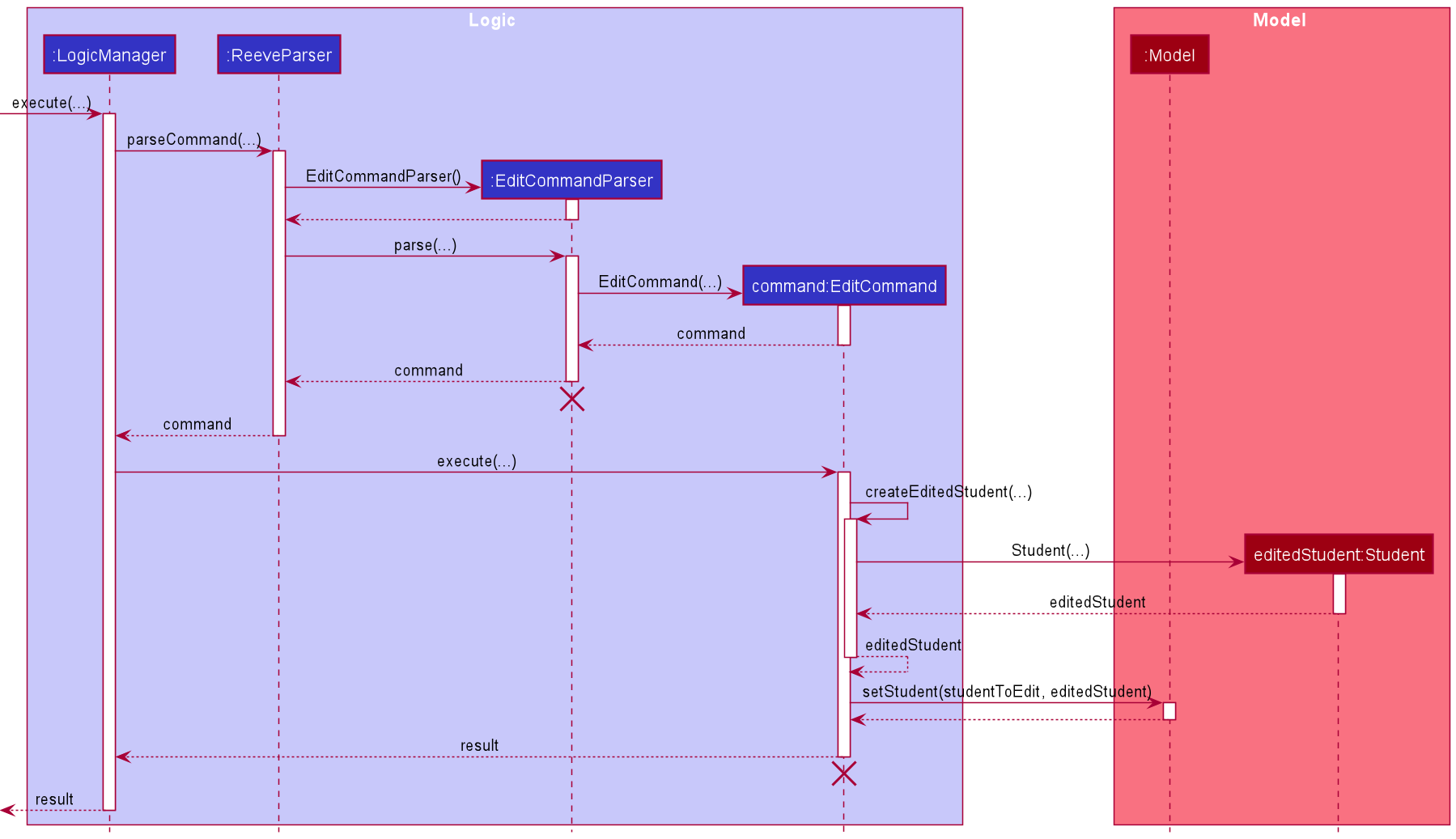
The following describes the flow of how EditCommand is executed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input, the
EditCommand#execute(Model model)is called which checks if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the student is not edited. - If there is such a student, the
EditCommand#execute(Model model)then creates the edited student, and checks to see if the edited student already exists in theUniqueStudentListusing theModel#hasStudent(Student toAdd). - If it is a duplicate student, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the edited student will not be added. - The
EditCommand#execute(Model model)also checks if the edited student has clashingClassTimewith other students already in theUniqueStudentList. - Two student’s
ClassTimeare considered clashing if they overlap either partially or fully. ACommandExceptionwill be thrown if there are other students with clashing class time. - If the edited student is not a duplicate and there are no clashes in class time, then the
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the outdated student with the edited copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the newly edited student. - The edited student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the EditCommand execution works.
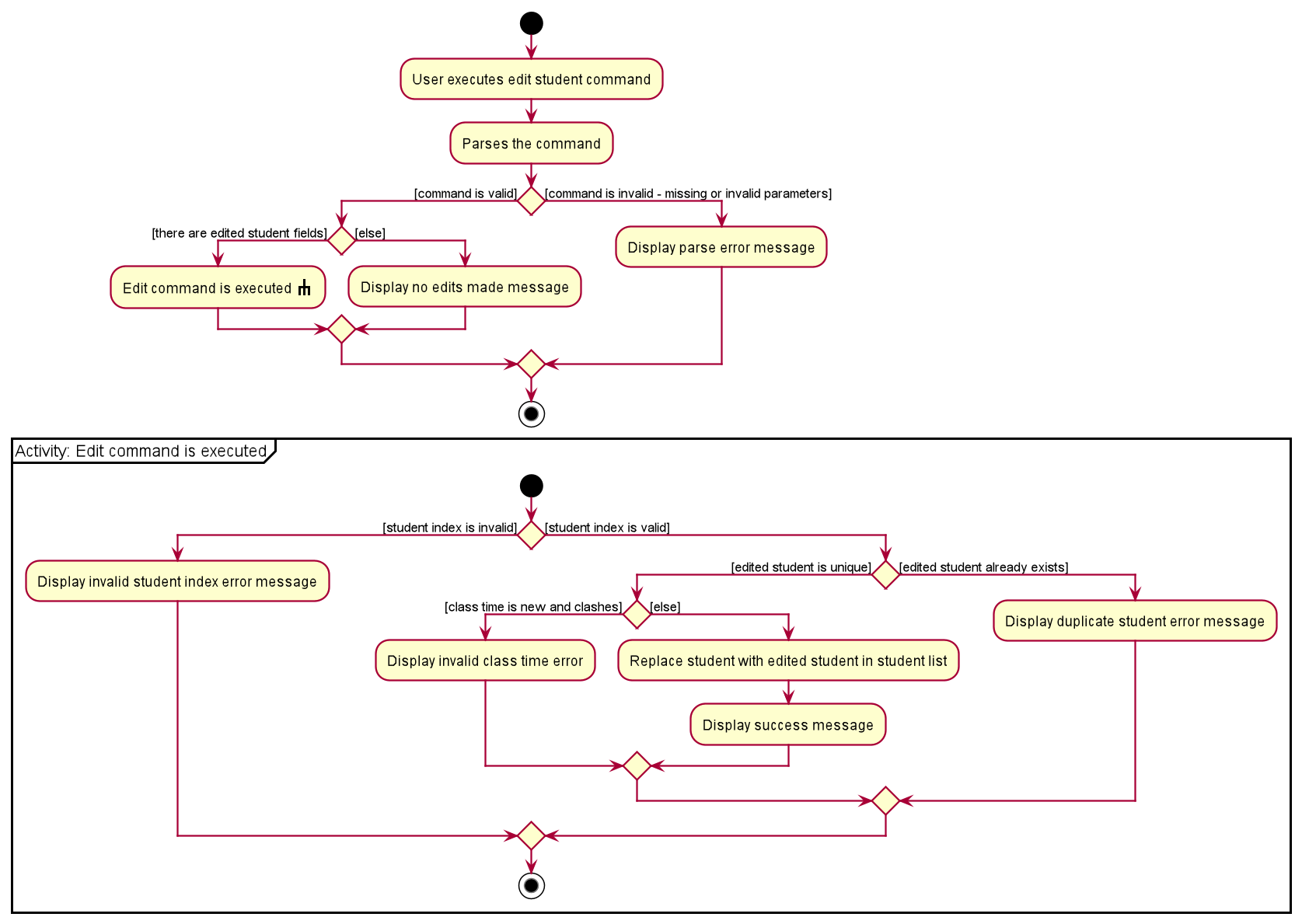
The following activity diagram summarizes the flow of events when the EditCommand is executed.
6.2.3 Delete Student Command
The following describes the flow of how DeleteCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input, the
DeleteCommand#execute(Model model)is called which checks whether the specifiedIndexis a valid index based on theUniqueStudentList, in the case where it is invalid, aCommandExceptionis thrown and no student will be deleted. - Otherwise, the
Studentat the specified validIndexis then removed from theUniqueStudentListusing theModel#deleteStudent(Student target)method. - The specified student is deleted from the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
![]() A valid
A valid Index is one that is within the bounds of the UniqueStudentList.
6.2.4 Find Student Command
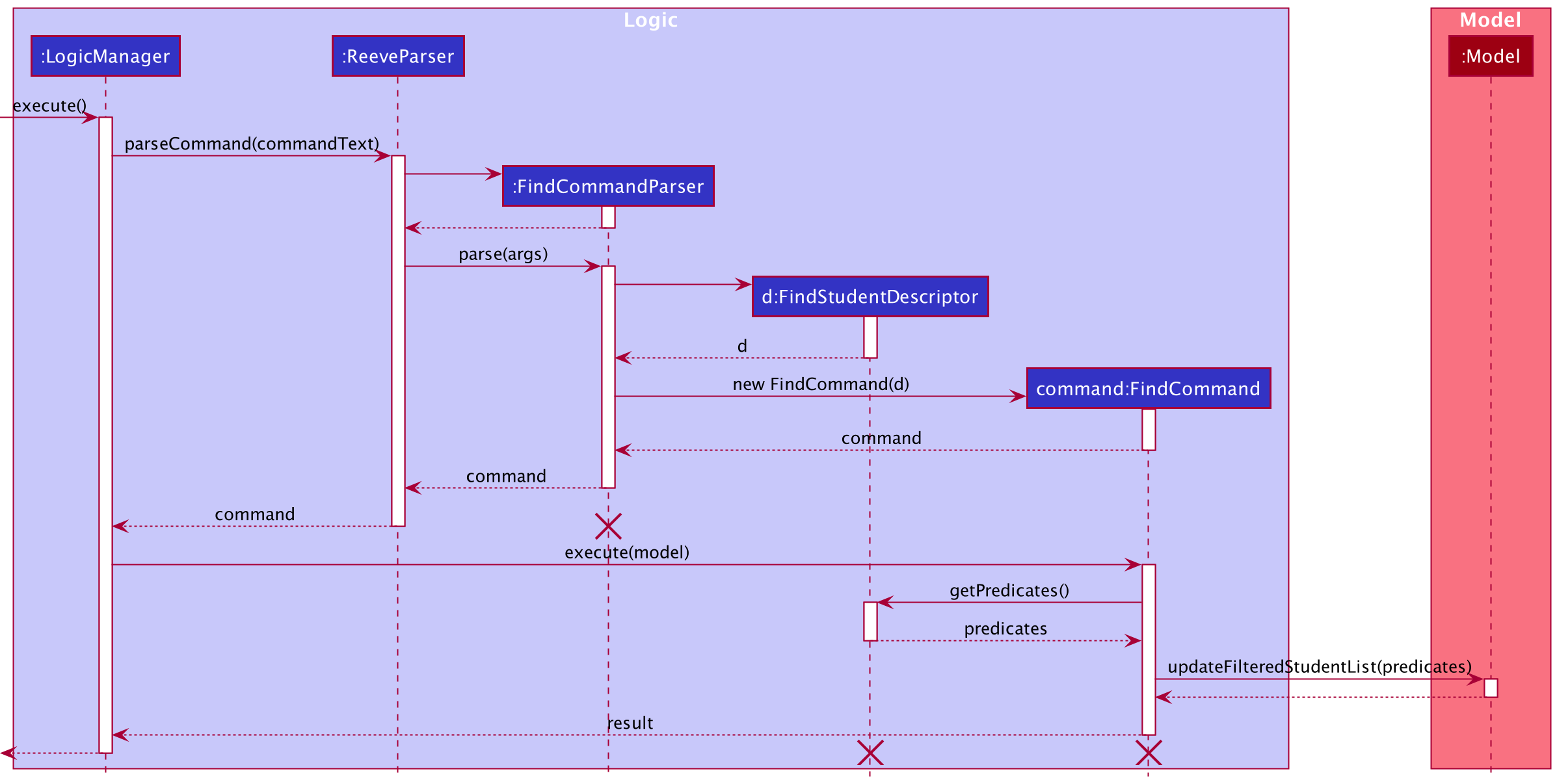
The following describes the flow of how FindCommand is performed.
- After the
FindCommandis created by parsing user input,FindCommand::executeis called. - The method then calls
getPredicates()of theFindStudentDescriptorstored withinFindCommandto obtain aList<Predicate>to search with. - The predicates within
List<Predicate>are then combined intoconsolidatedPredicate. - The
FilteredList<Student>within theModelis then updated usingModel#updateFilteredPersonList(Predicate predicate)for display. - A new
CommandResultwill be returned with the success message.
The following sequence diagram shows how the FindCommand execution works.
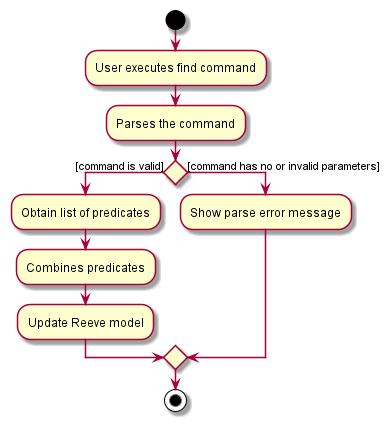
The following activity diagram summarizes the flow of events when the FindCommand is executed.
6.2.5 Overdue Command
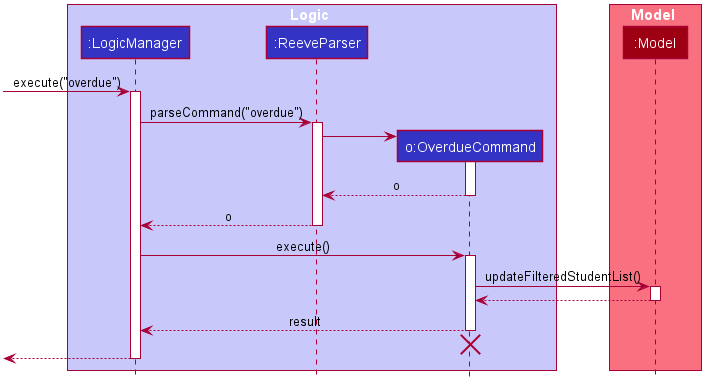
The overdue payment filter feature allows the tutor to find all students who have not paid their tuition fees in the past month. It is handled by the OverdueCommand.
The following describes the flow of how OverdueCommand is executed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
OverdueCommand#execute(Model model)is called to filter all students in Reeve whose last date of payment was more than a month ago. -
Model#updateFilteredStudentsList(Predicate<Student> predicate)is called to find only students that match the above condition. A newCommandResultis returned with a successful message indicating the number of matching students. - The filtered student list replaces the displayed list on the GUI and a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the OverdueCommand execution works.
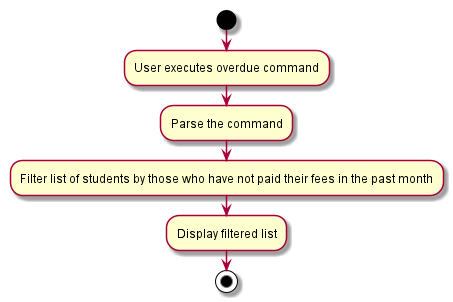
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when OverdueCommand is executed.
6.2.6 Detail Commands
The Detail commands keep track of any additional details a tutor wants to add to a student. They comprise of the following commands:
-
AddDetailCommand- Adds a detail to a specified student. -
EditDetailCommand- Edits a specified detail in a specified student. -
DeleteDetailCommand- Deletes a specified detail from a specified student.
6.2.6.1 Add Detail Command
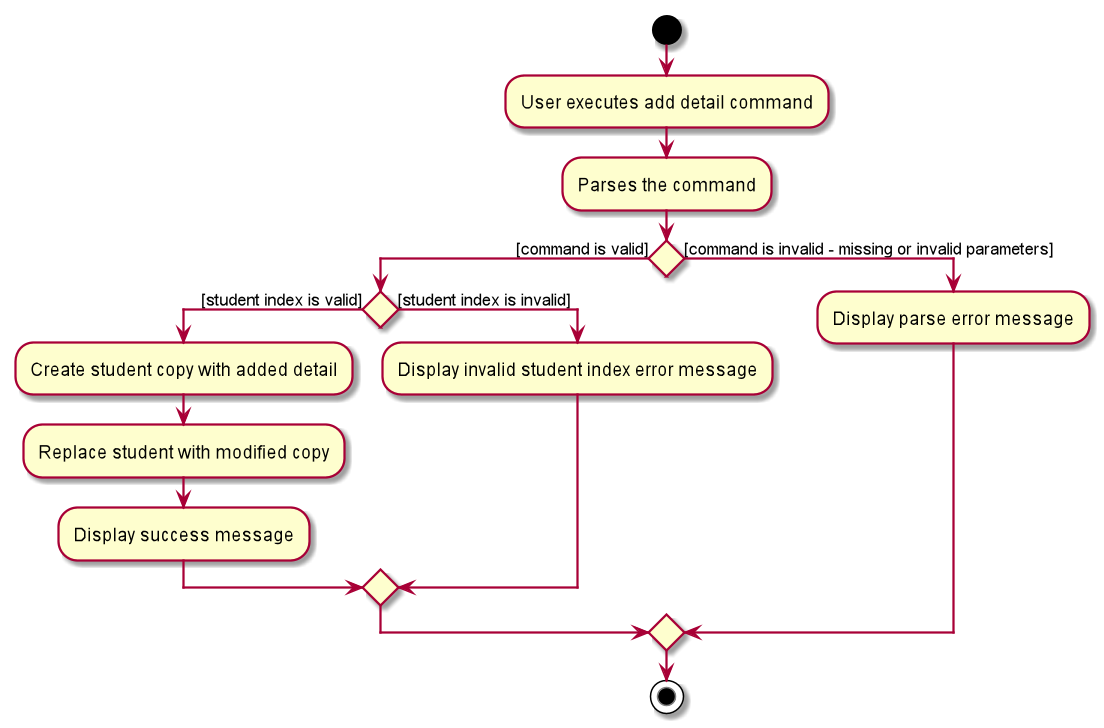
The following describes the flow of how AddDetailCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
AddDetailCommand#execute(Model model), and it checks if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the detail will not be added. - If the student exists, the detail is added to the student’s list of details, and
DetailCommand#updateStudentDetail(Student studentToAddDetail, List<Detail> details)is called to create a modified copy of the student with the new detail. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the detail added. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the detail adding operation works.
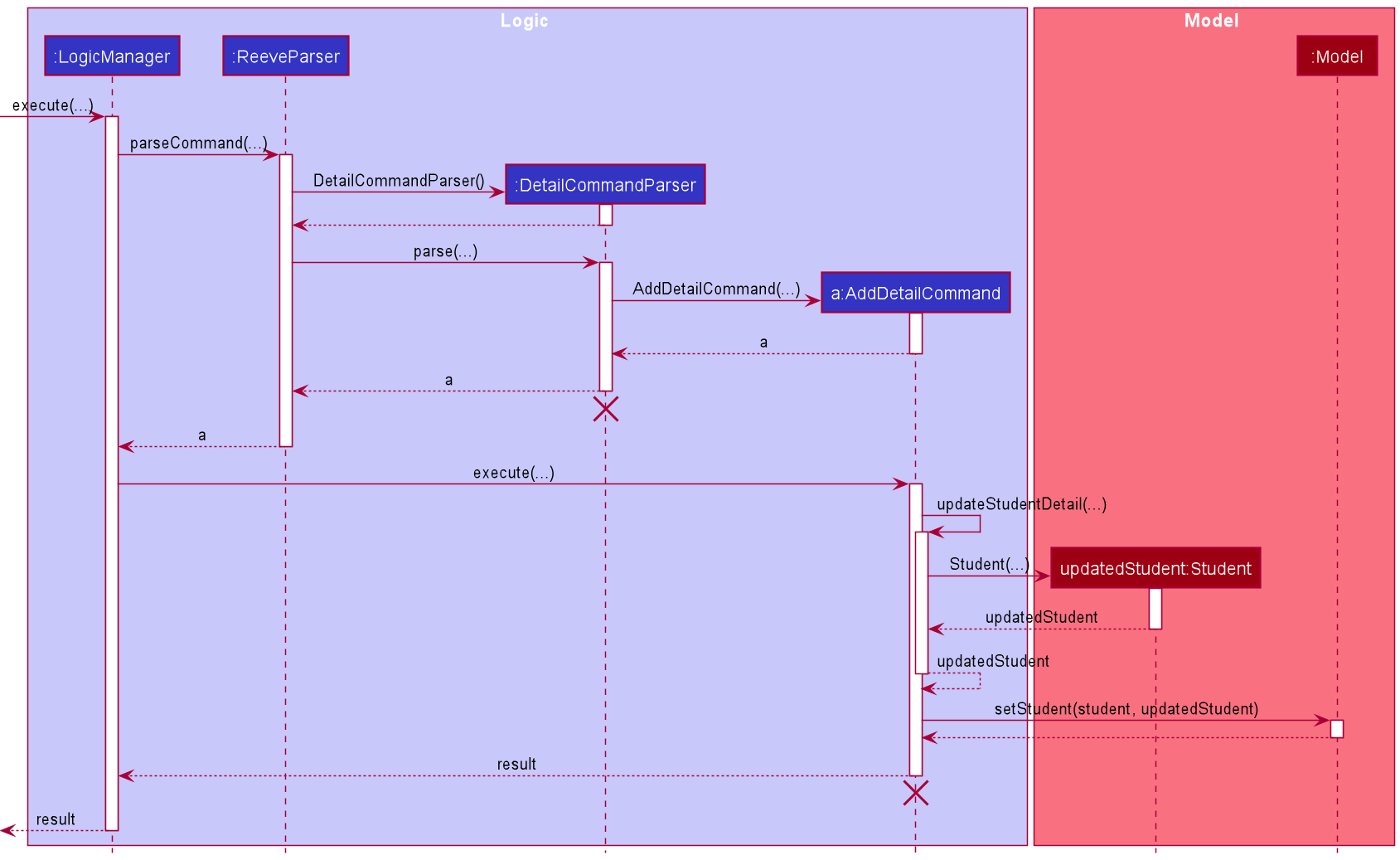
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when AddDetailCommand is executed.
6.2.6.2 Edit Detail Command
The following describes the flow of how EditDetailCommand is performed.
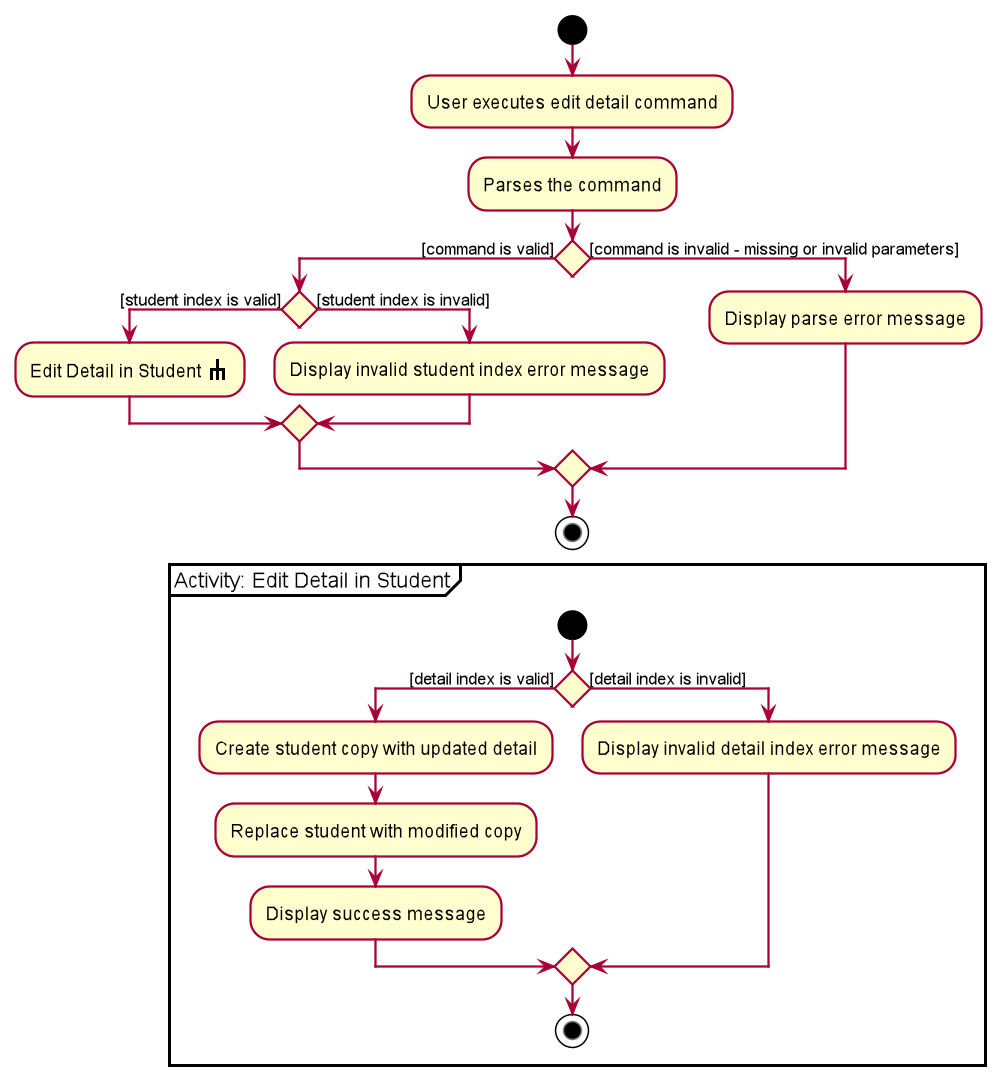
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
EditDetailCommand#execute(Model model), and it checks if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the detail will not be edited. - If the student exists,
EditDetailCommand#execute(Model model)then checks if the detail at the specified position exists. - If there is no detail at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the detail will not be edited. - If the detail exists, the newly updated detail is added to the student’s list of details, and
DetailCommand#updateStudentDetail(Student studentToEditDetail, List<Detail> details)is called to create a modified copy of the student with the new detail. -
Student#addQuestion(Question question)is called to create a modified copy of the student with a newly added question. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the detail added. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the detail editing operation works.
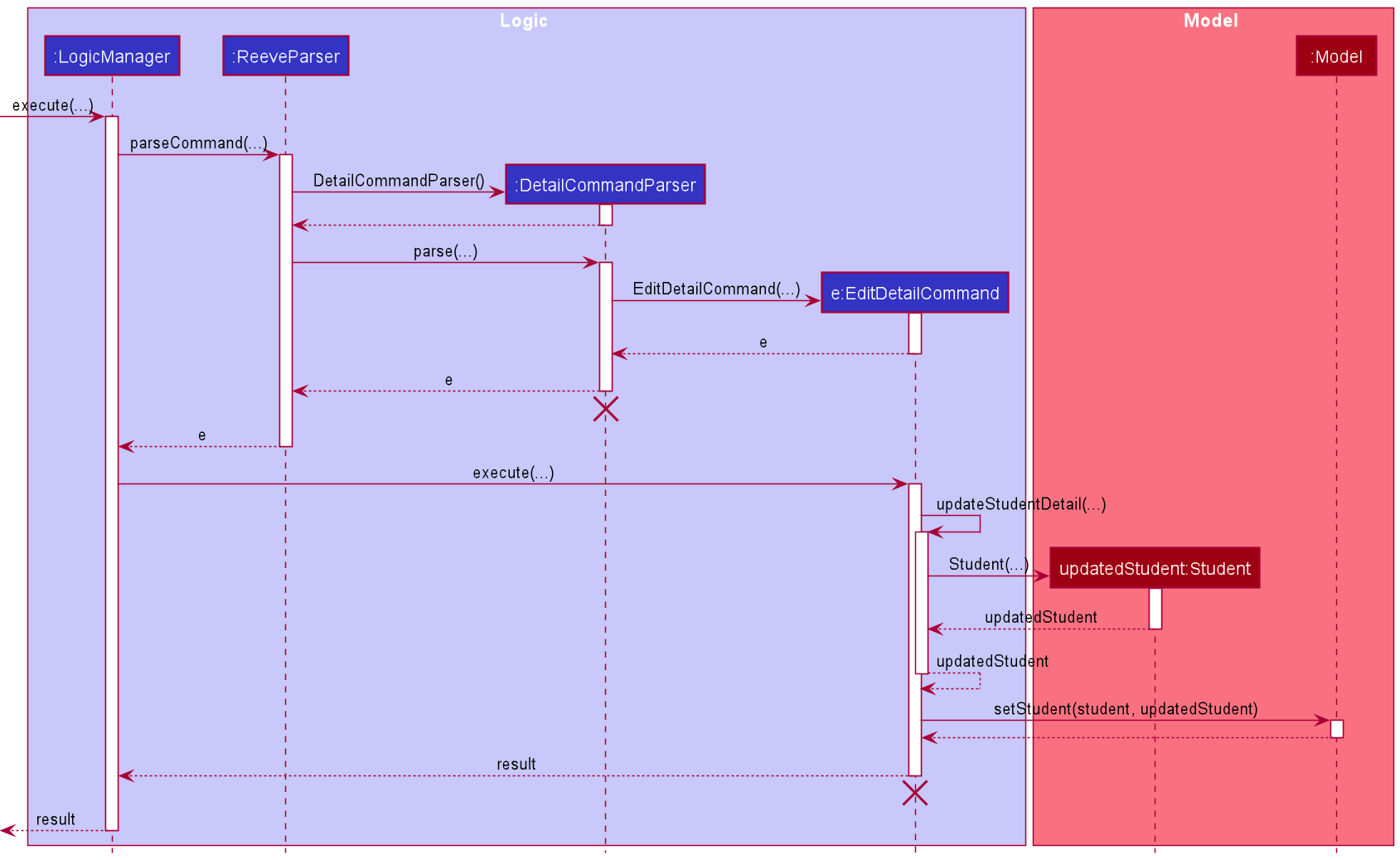
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when EditDetailCommand is executed.
6.2.6.3 Delete Detail Command
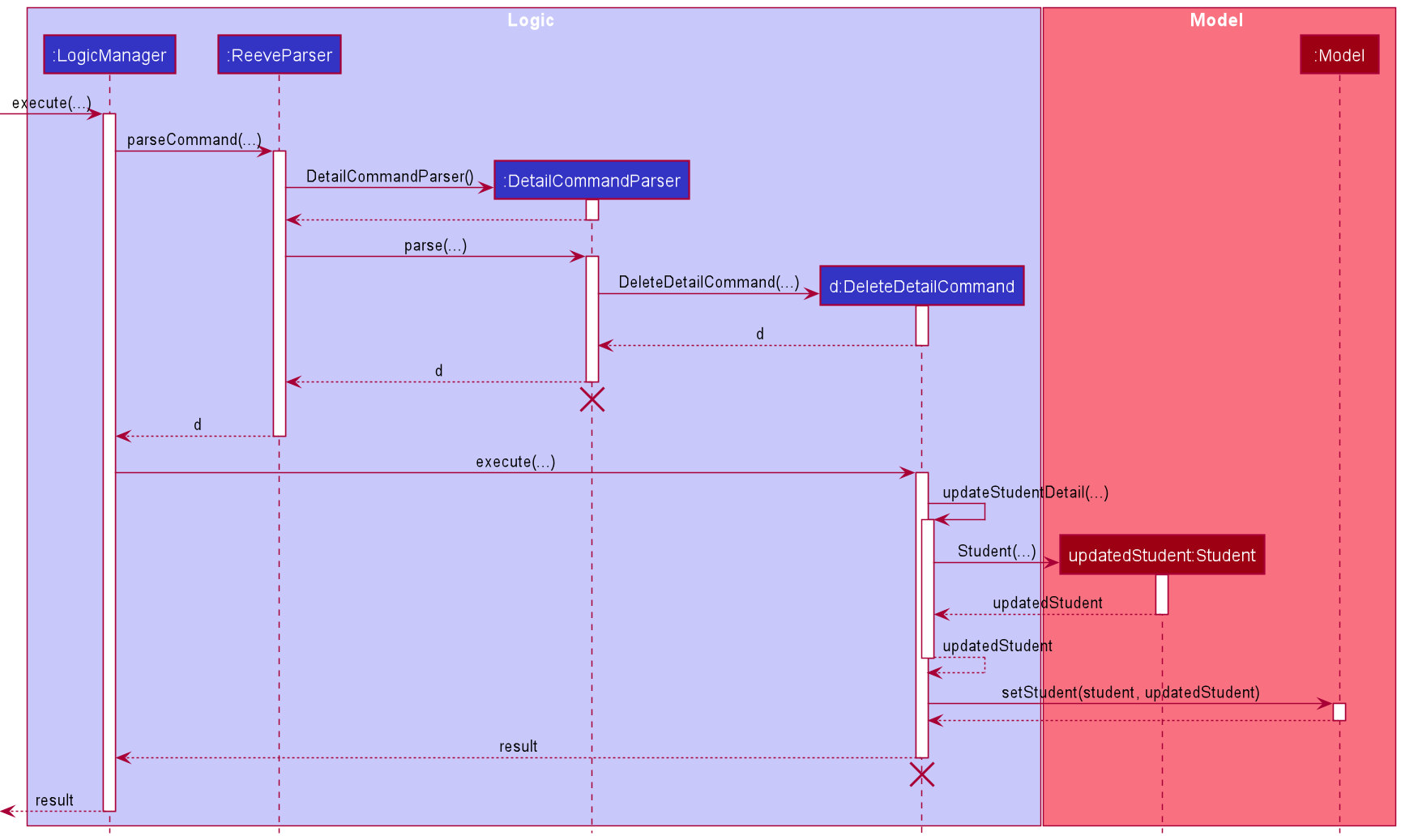
The following describes the flow of how DeleteDetailCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
DeleteDetailCommand#execute(Model model), and it checks if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the detail will not be deleted. - If the student exists,
DeleteDetailCommand#execute(Model model)then checks if the detail at the specified position exists. - If there is no detail at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the detail will not be deleted. - If the detail exists, the detail is removed from the student’s list of details, and
DetailCommand#updateStudentDetail(Student studentToDeleteDetail, List<Detail> details)is called to create a modified copy of the student with detail removed. -
Student#addQuestion(Question question)is called to create a modified copy of the student with a newly added question. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the removed detail. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the detail deleting operation works.
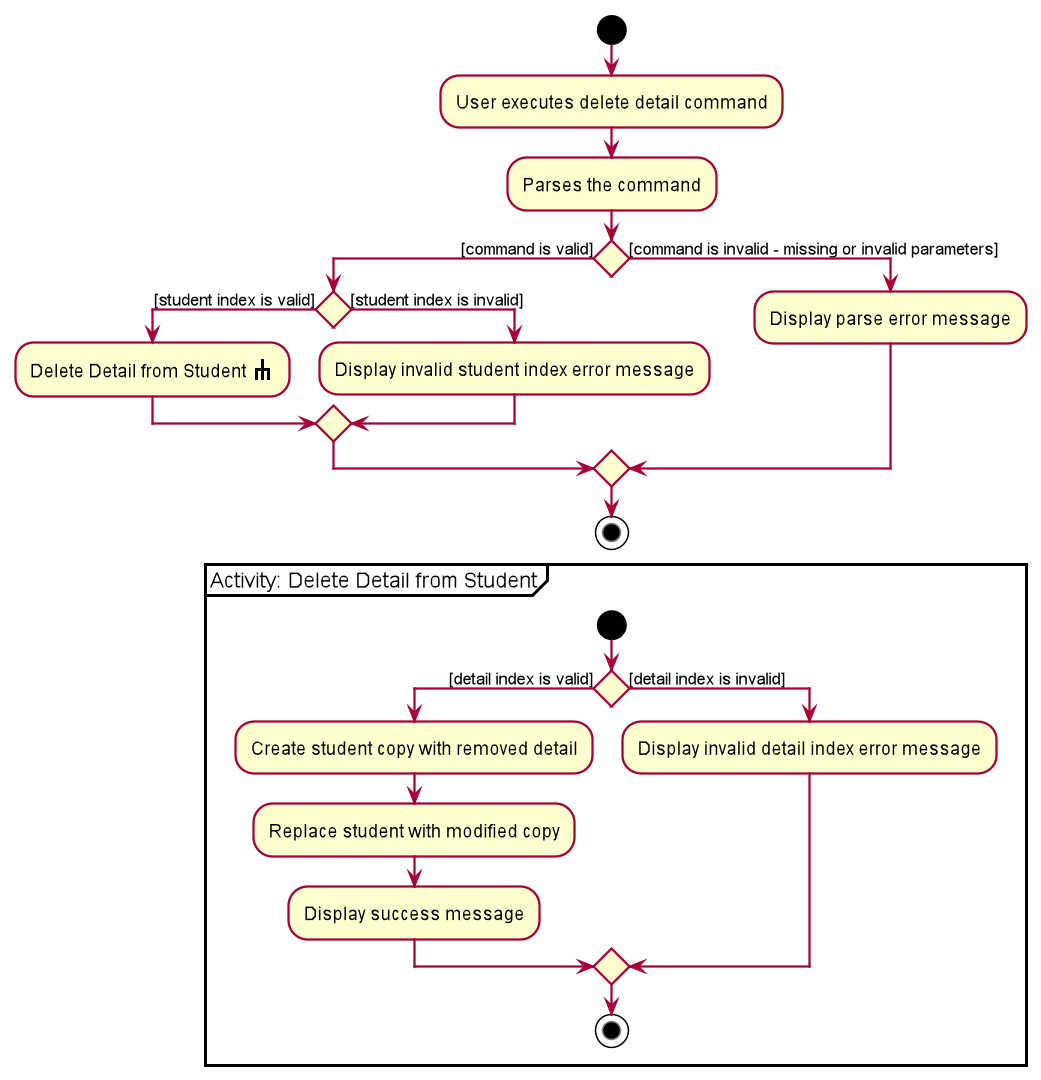
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when DeleteDetailCommand is executed.
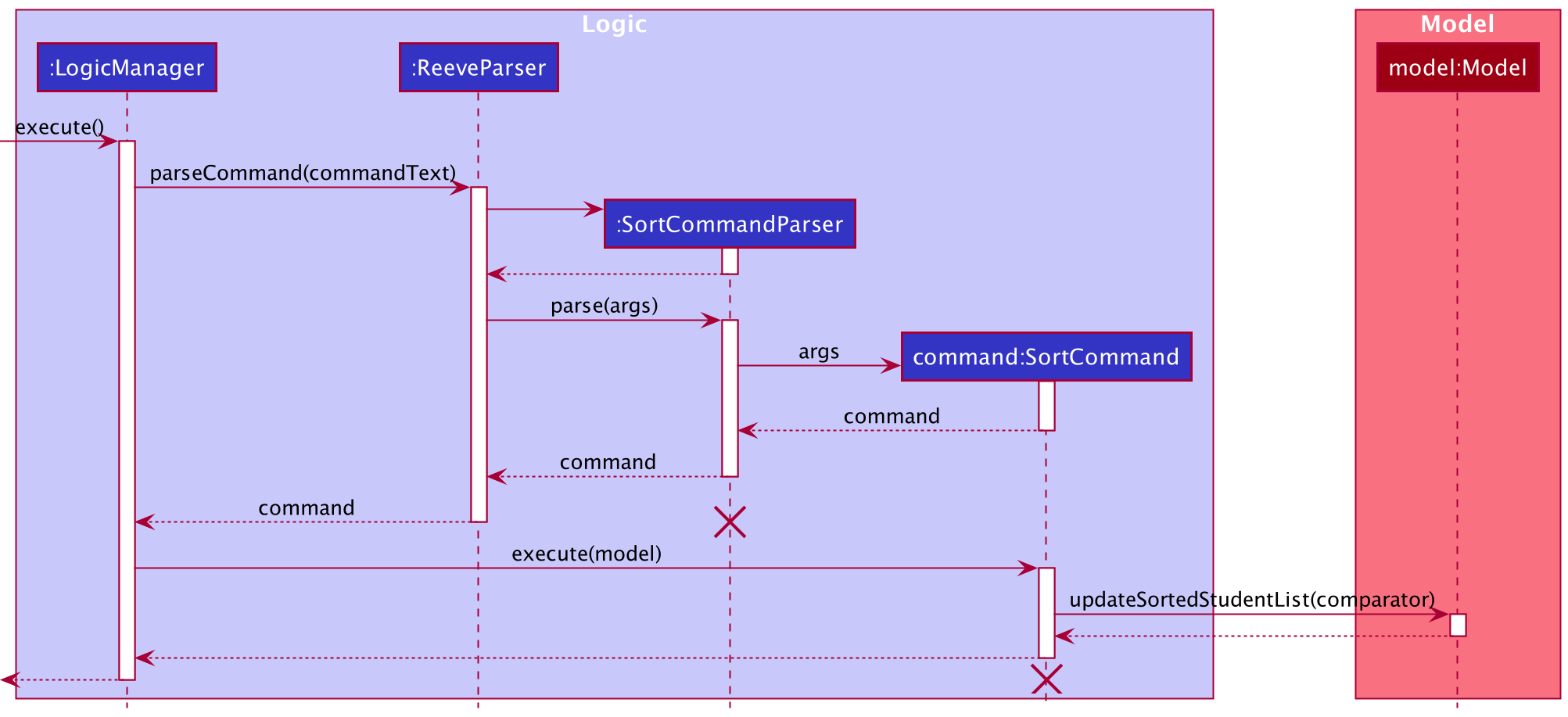
6.2.7 Sort Command
This is an explanation of how SortCommand works.
- After the
SortCommandis successfully parsed,SortCommand#execute(Model model)is called to execute the command. - The
comparisonMeansstored within theSortCommandis checked againstNameComparator.COMPARISON_MEANS,ClassTimeComparator.COMPARISON_MEANSandYearComparator.COMPARISON_MEANS. - If
comparisonMeansmatches the comparison means ofNameComparator,NameComparator.COMPARISON_MEANS, a newNameComparatoris created andModel#updateSortedStudentList(Comparator<? extends Student> comparator)called. - Step 3 is repeated similarly for
ClassTimeComparatorandYearComparator. - If
comparisonMeansmatches no comparison means in steps 3 and 4, aCommandExceptionis thrown. - The student list is sorted and a
CommandResultwith the success message is returned.
The following sequence diagram shows how the SortCommand execution works.
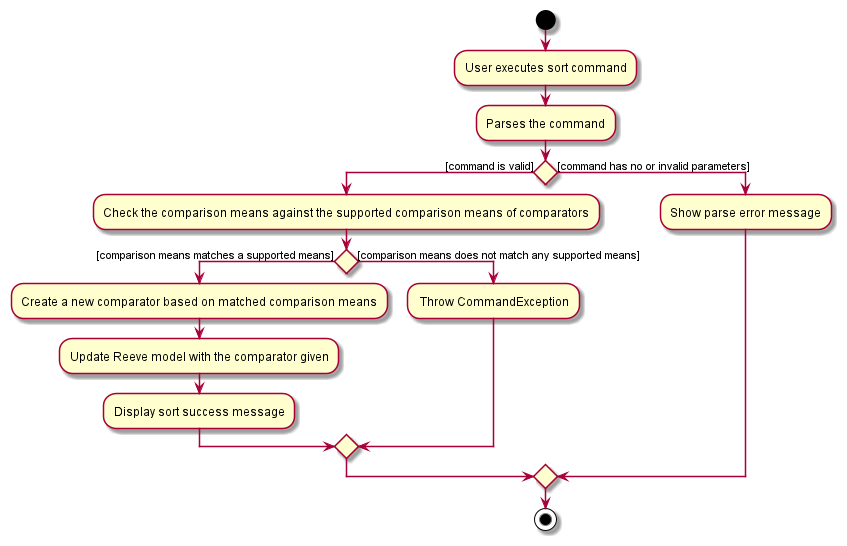
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when SortCommand is executed.
6.3 Student academic details features
This section describes some key details on how academic details features are implemented.
6.3.1 Question Commands
The Question commmands keep track of questions raised by a student to his tutor. They comprise of the following commands:
-
AddQuestionCommand- Adds a question to a specified student. -
SolveQuestionCommand- Marks a specified question from a specified student as solved. -
DeleteQuestionCommand- Deletes a specified question from a specified student.
6.3.1.1 Add Question Command
The following describes the flow of how AddQuestionCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
AddQuestionCommand#execute(Model model)is called to check if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the question will not be added. - If the student exists,
AddQuestionCommand#execute(Model model)checks if the student already has a similar question recorded. - A unique question is defined solely by its
questionand does not take into account if the question has been solved. If a duplicate question is found, aCommandExceptionis thrown and the question will not be added. - If the question is not a duplicate,
Student#addQuestion(Question question)is called to create a modified copy of the student with a newly added question. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the question added. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the question adding operation works.
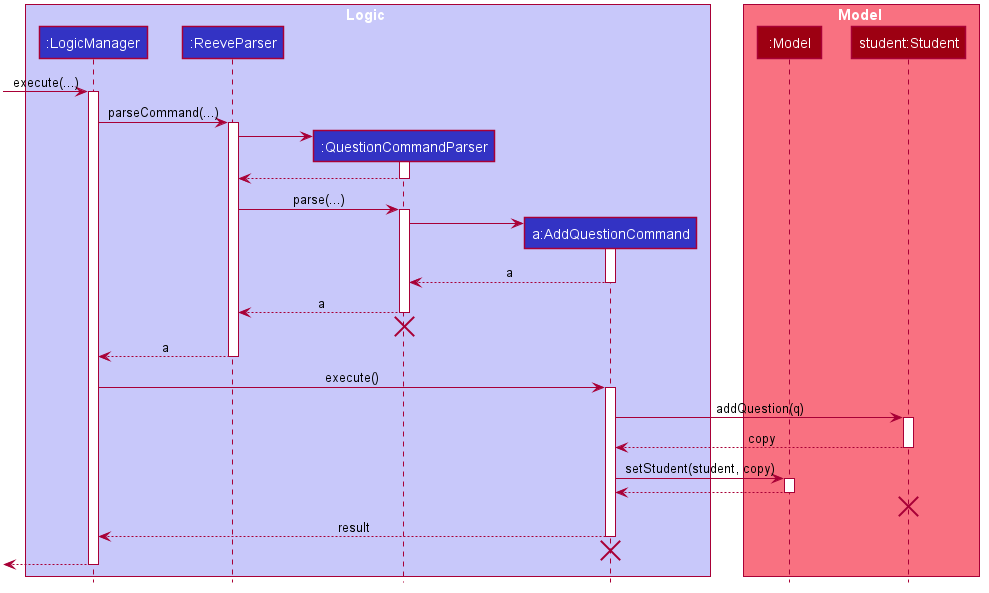
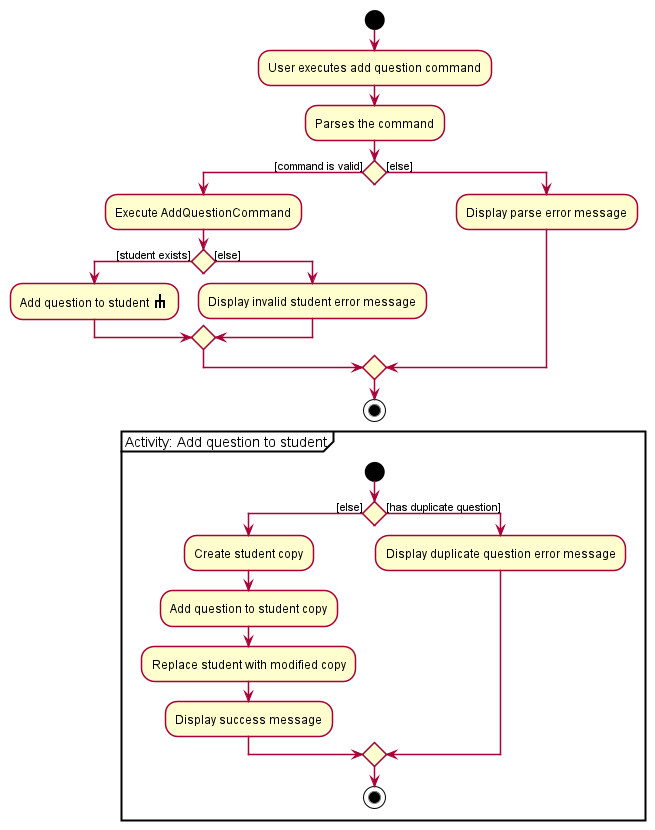
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when AddQuestionCommand is executed.
6.3.1.2 Solve Question Command
The following describes the flow of how SolveQuestionCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
SolveQuestionCommand#execute(Model model)is called to check if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the question will not be added. - If the student exists,
SolveQuestionCommand#execute(Model model)checks if there is a question at the specified position. - If the question does not exist, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the question will not be resolved. - If the question exists,
Student#setQuestion(Question target, Question newQuestion)is called to create a modified copy of the student where the specified question has been replaced with a solved version. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the question solved. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the question solving operation works.
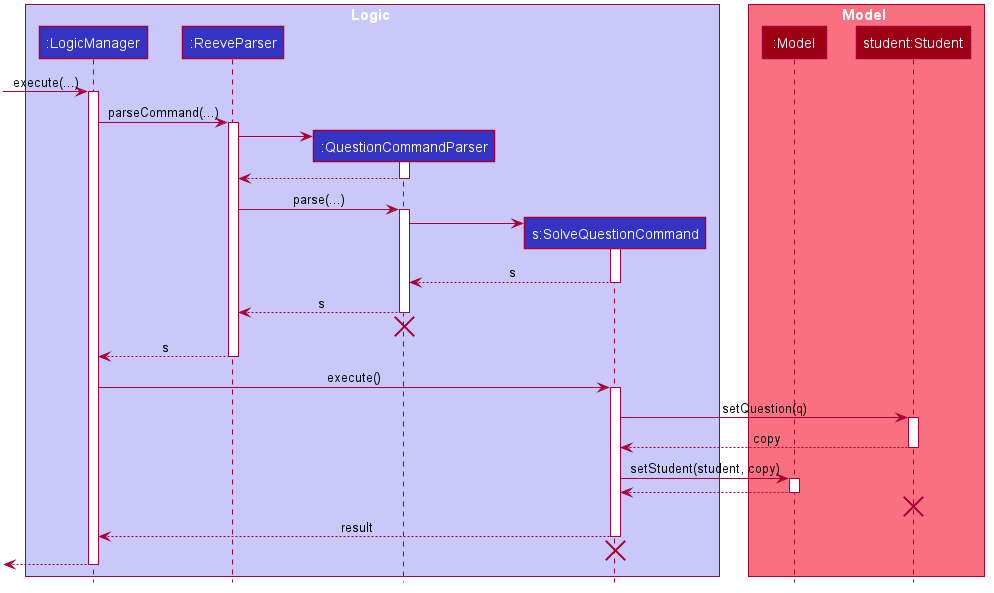
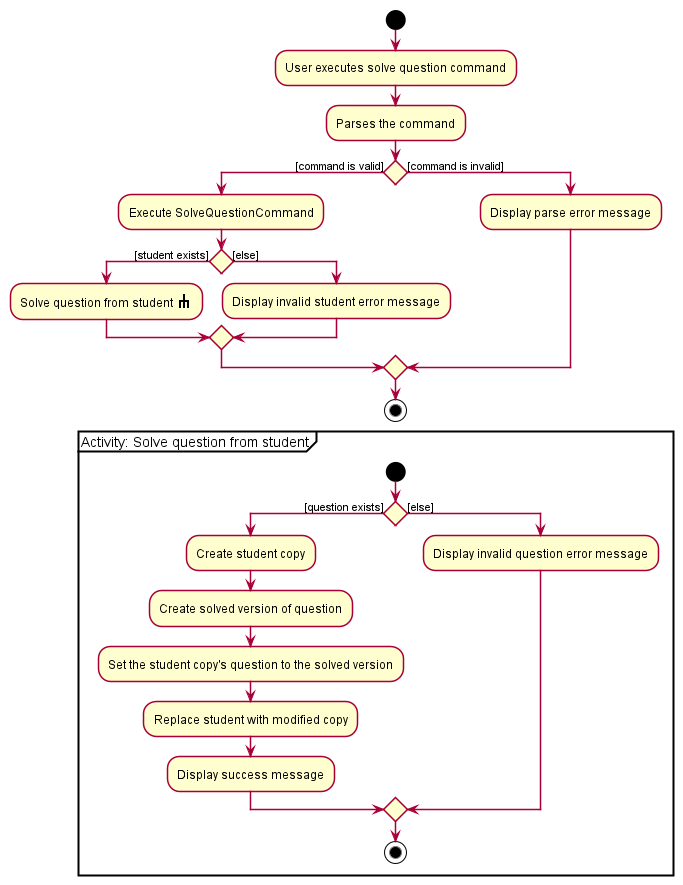
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when SolveQuestionCommand is executed.
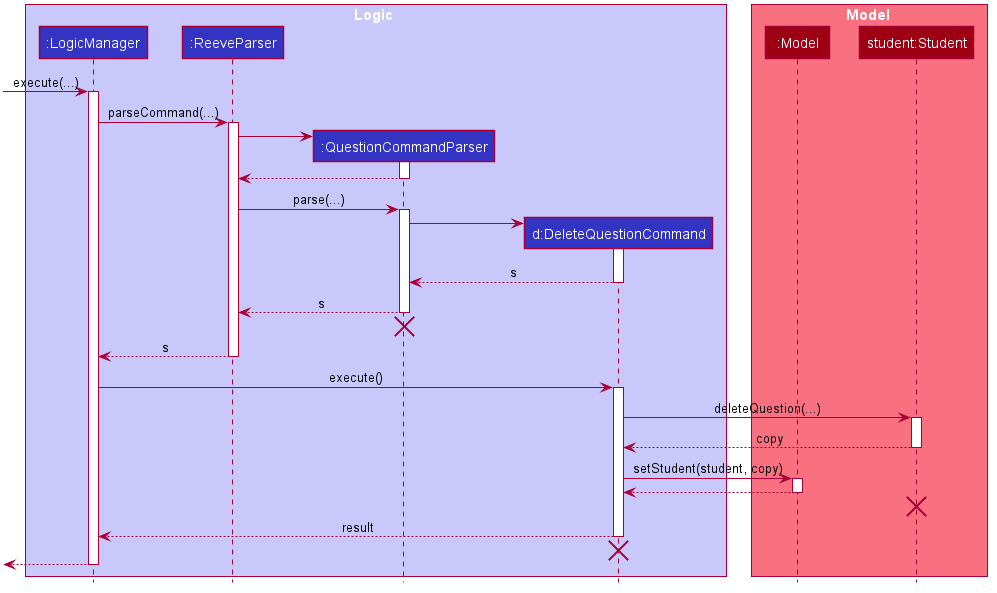
6.3.1.3 Delete Question Command
The following describes the flow of how DeleteQuestionCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
DeleteQuestionCommand#execute(Model model)is called to check if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the question will not be added. - If the student exists,
DeleteQuestionCommand#execute(Model model)checks if there is a question at the specified position. - If the question does not exist, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the question will not be resolved. - If the question exists,
Student#deleteQuestion(Question target)is called to create a modified copy of the student without the specified question. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the question removed. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the question deletion operation works.
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when DeleteQuestionCommand is executed.
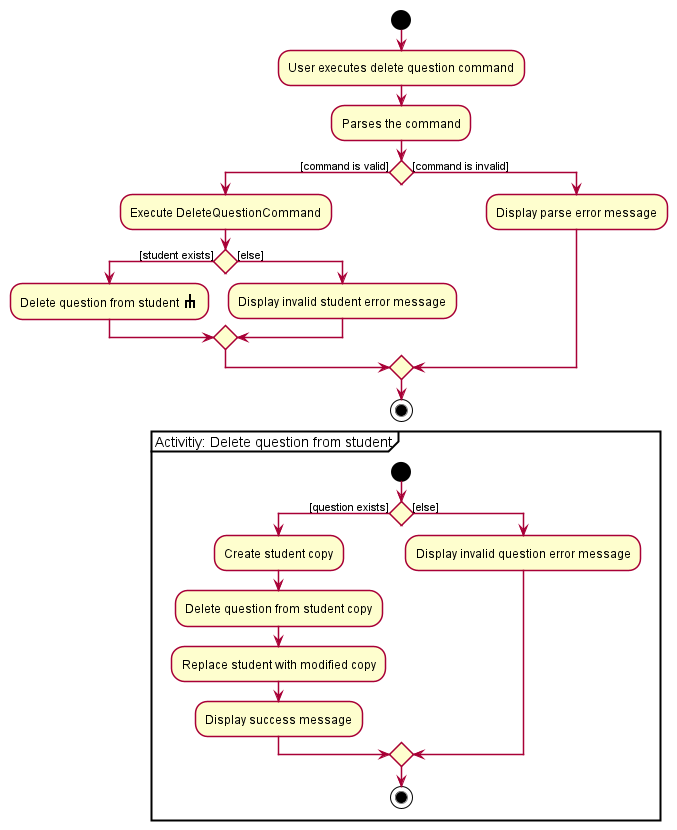
6.3.1.4 Design considerations
The Student class guarantees immutability, including its list of Question objects. As such, any operation must return a modified copy instead of directly modifying the base list.
The pros of doing so is that it becomes easier to test and debug as there are fewer mutations to worry about.
The downside, however, that this approach is more memory-intensive and possibly slower, since changing a single question involves recreating the entire list of questions attached to the student.
Having considered that our target audience (one-to-one private tutors) are unlikely to have so much data that this would severely impact performance, we believe that this is worth the trade-off.
6.3.2 Exam Commands
The Exam commands keep track of exam records of a student. They comprise of the following commands:
-
AddExamCommand- Adds a exam record to a specified student. -
DeleteExamCommand- Deletes a specified exam record from a specified student. -
ExamStatsCommand- Displays the exam statistics of a specified student in the form of a line graph.
The structure of exam commands is as shown below:
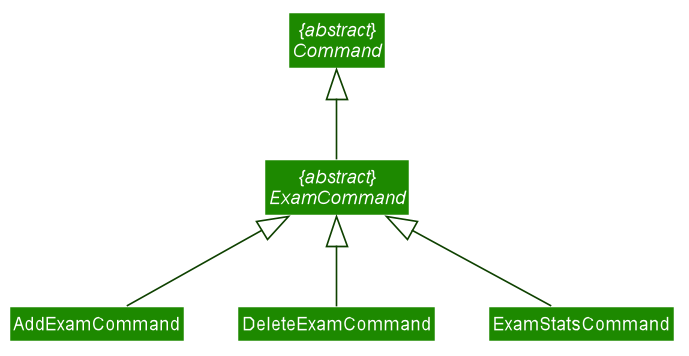
6.3.2.1 Add exam command
The following describes the flow of how AddExamCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
AddExamCommand#execute(Model model)is called to check if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the exam will not be added. - If the student exists,
AddExamCommand#execute(Model model)checks if the student already has a similar exam recorded. - A unique exam is defined solely by its
examName. If a duplicate exam is found, aCommandExceptionis thrown and the exam will not be added. - If the exam is not a duplicate,
Student#getExams()is called get the current list of exams of the specified student. - The new exam is added into this current list and a new updated
Studentis created which has exactly the same characteristics as the specified student but with the updated exam list. -
Model#setStudent(Student selectedStudent, Student updatedStudent)is called to replace the student with the updated copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the exam added. - The updated student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The sequence and activity diagrams are very similar to those of the detail adding command
6.3.2.2 Delete exam command
The following describes the flow of how DeleteExamCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
DeleteExamCommand#execute(Model model)is called to check if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown. - If the student exists,
DeleteExamCommand#execute(Model model)checks if there is a exam at the specified position. - If the exam does not exist, a
CommandExceptionis thrown. - If the exam exists,
Student#getExams()is called get the current list of exams of the specified student. -
Model#setStudent(Student selectedStudent, Student updatedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the exam removed. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
![]() Exams are specified based on the indexes of the list of exams shown on the academic view of student details.
Exams are specified based on the indexes of the list of exams shown on the academic view of student details.
The sequence and activity diagrams are very similar to those of the detail deleting command
6.3.2.3 Exam Stats command
The following describes the flow of how ExamStatsCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
ExamStatsCommand#execute(Model model)is called to check if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and no exam statistics window will be shown. - If the student exists,
ExamStatsCommand#execute(Model model)gets the specified student fromsortedStudentList. - A
CommandResultwith a non-null student input is returned andMainWindow#handleExamStats(Student student)is called. - A new ExamStats display window will be opened showing a line graph representing the exam scores of the specified student.
The following sequence diagram shows how the exam stats operation works.
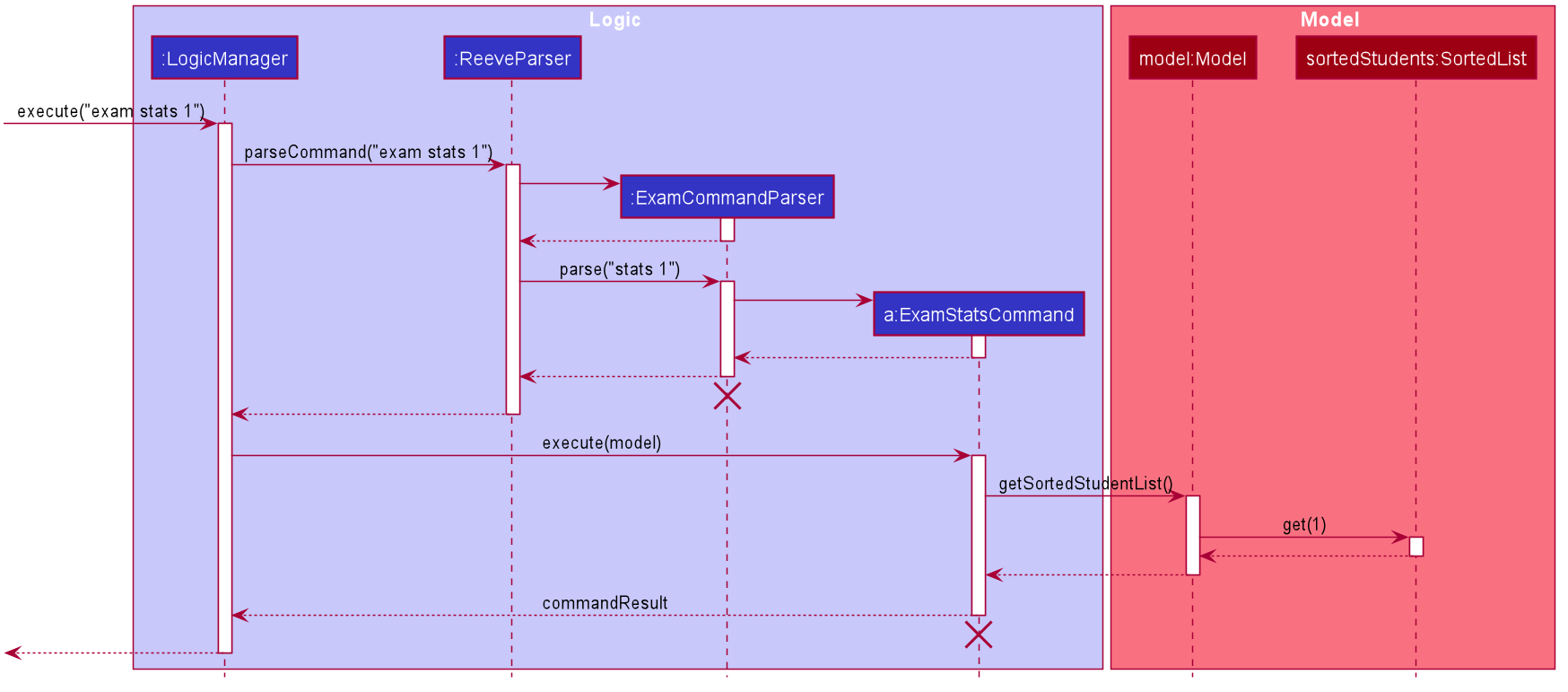
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when ExamStatsCommand is executed.
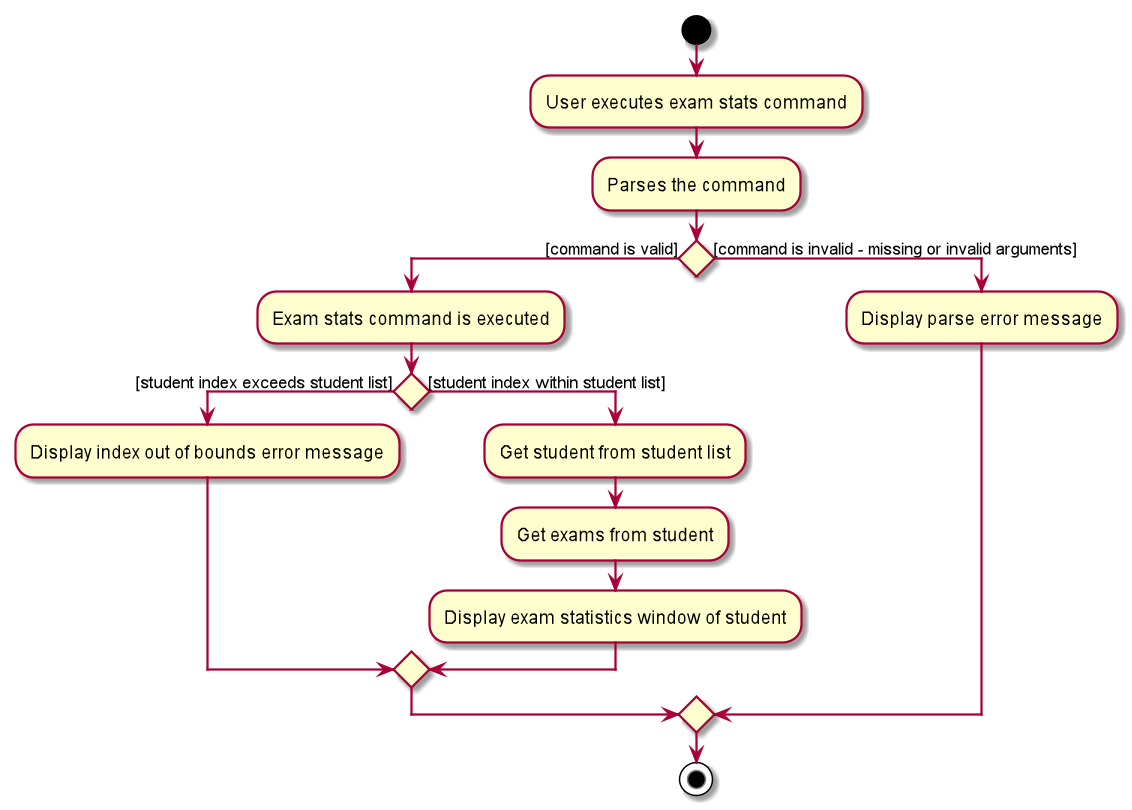
The following explains the design considerations of the exam stats command.
Aspect: How the GUI responds when exam stats is executed
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Open new window that displays exam statistics.
- Pros: Easy to implement, allows for comparison and reference with student data, allows for multiple students’ exam statistics to be opened, easy for users to understand.
- Cons: Can be more taxing on processor if many windows are opened simultaneously
-
Alternative 2: Switch from the displayed student list panel to an exam statistics panel.
- Pros: Only one window open at all time.
- Cons: Unable to compare and reference with student data, harder to implement, can introduce confusion when trying to switch back to the student list panel.
6.3.3 Attendance Commands
The Attendance commands keep track of the attendance for a student. They comprise of the following commands:
-
AddAttendanceCommand- Adds an attendance to a specified student. -
DeleteAttendanceCommand- Deletes a specified attendance from a specified student.
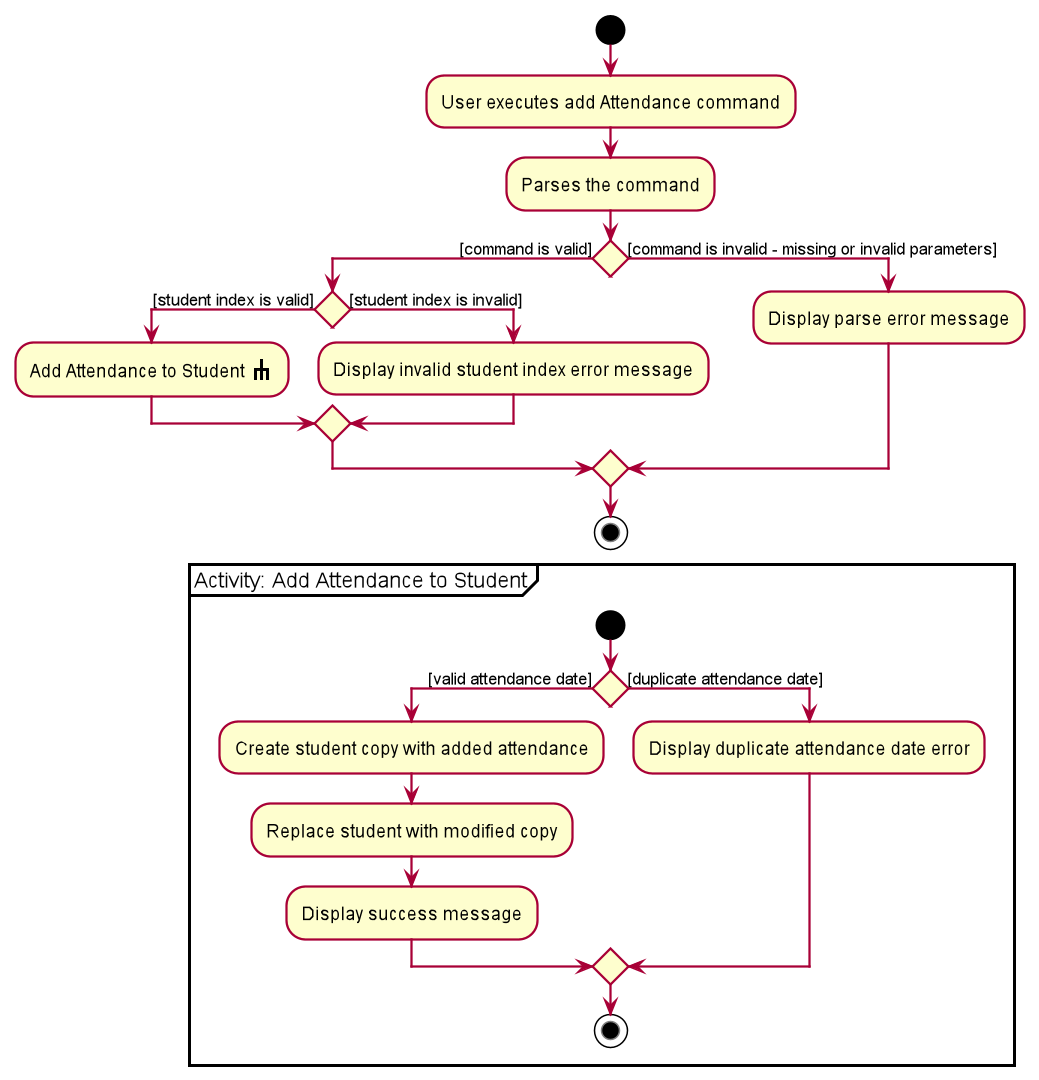
6.3.3.1 Add Attendance Command
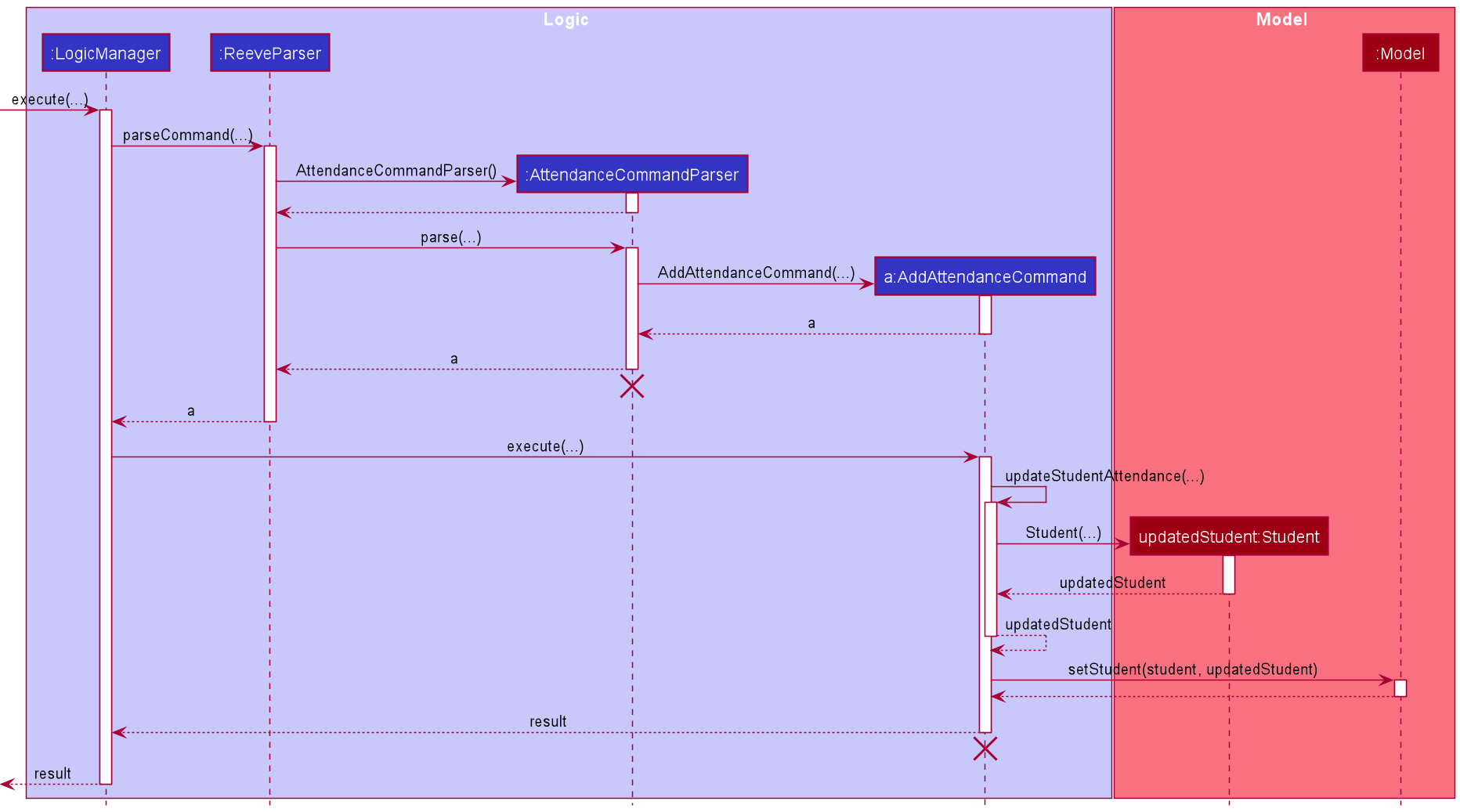
The following describes the flow of how AddAttendanceCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
AddAttendanceCommand#execute(Model model), and it checks if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the attendance will not be added. - If the student exists,
AddAttendanceCommand#execute(Model model)then checks if the student has an existing attendance with the input attendance date. - If there is such an attendance, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the attendance will not be added. - If there is no such attendance, the attendance is added to the student’s list of attendances, and
AttendanceCommand#updateStudentAttendance(Student studentToAddAttendance, List<Attendance> attendances)is called to create a modified copy of the student with the new attendance. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the attendance added. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the attendance adding operation works.
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when AddAttendanceCommand is executed.
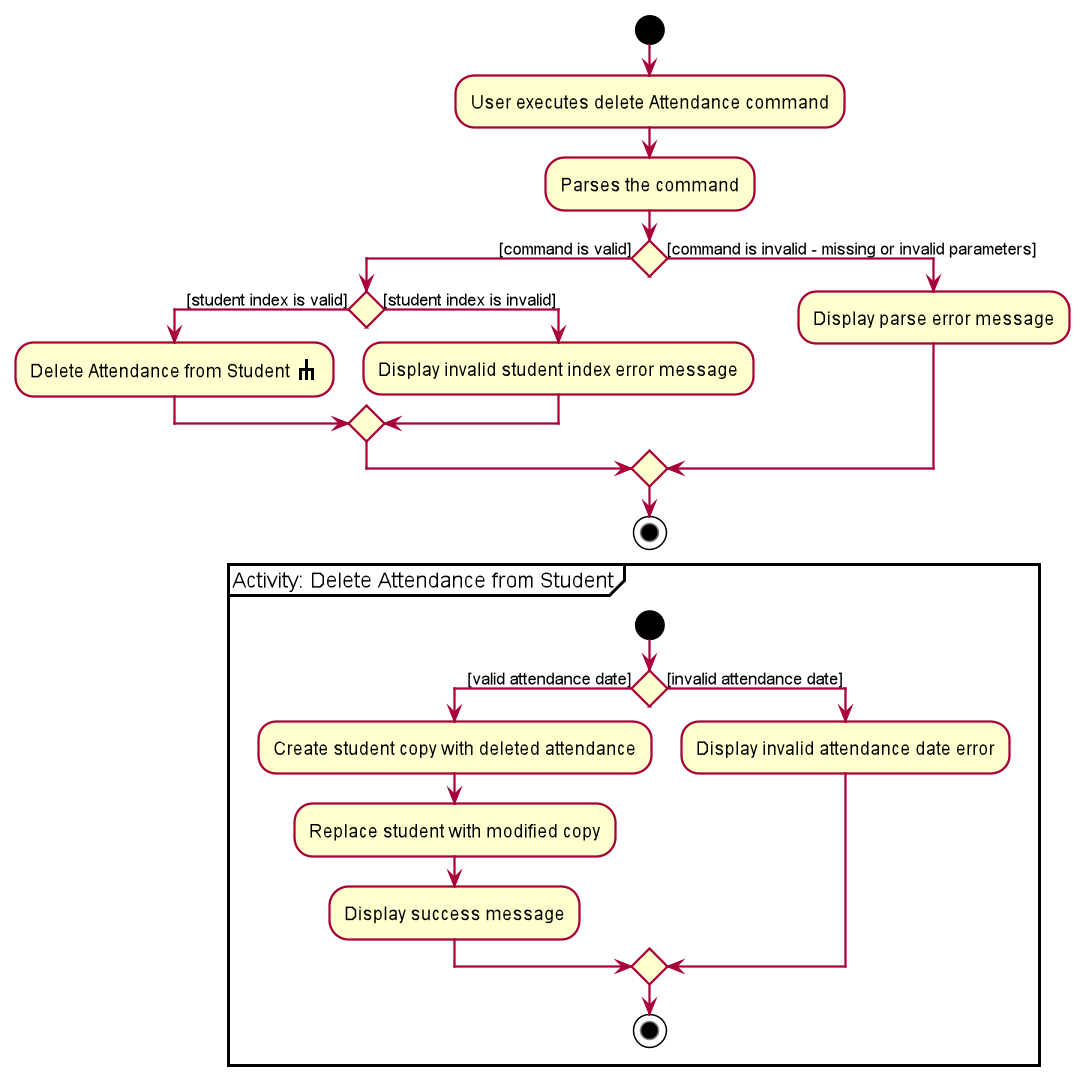
6.3.3.2 Delete Attendance Command
The following describes the flow of how DeleteAttendanceCommand is performed.
- Upon successfully parsing the user input,
DeleteAttendanceCommand#execute(Model model), and it checks if the student at the specified position exists. - If there is no student at the specified position, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the attendance will not be deleted. - If the student exists,
DeleteAttendanceCommand#execute(Model model)then checks if the student has an existing attendance with the input attendance date. - If there is no such attendance, a
CommandExceptionis thrown and the attendance will not be deleted. - If there is such an attendance, the attendance is deleted from the student’s list of attendances, and
AttendanceCommand#updateStudentAttendance(Student studentToDeleteAttendance, List<Attendance> attendances)is called to create a modified copy of the student with attendance removed. -
Model#setStudent(Student target, Student editedStudent)is called to replace the student with the modified copy. A newCommandResultis returned with a success message showing the affected student and the attendance deleted. - The modified student replaces the outdated student in the
UniqueStudentListand a success message is shown in the result display.
The following sequence diagram shows how the attendance deleting operation works.
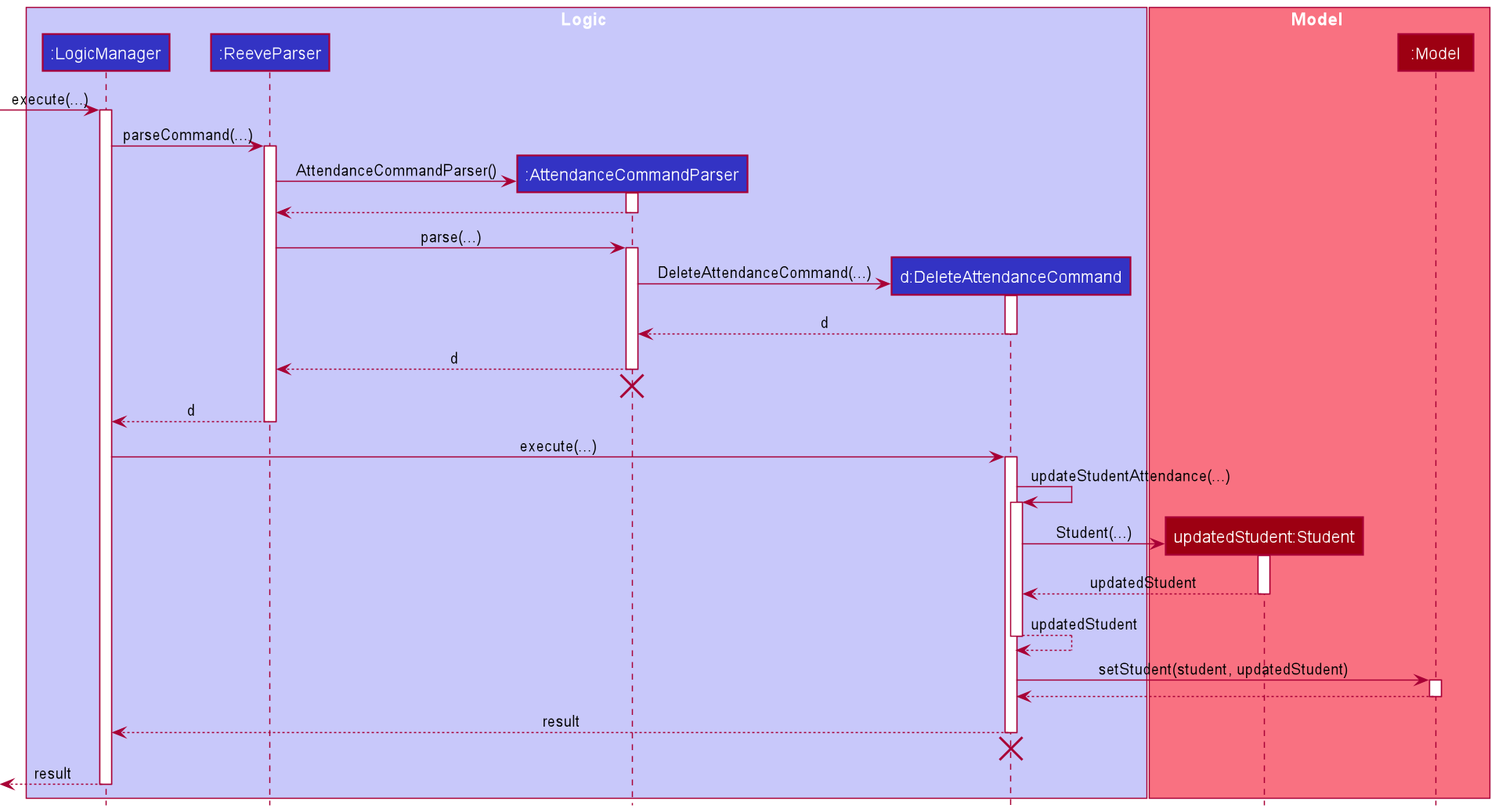
The following activity diagram summarises the flow of events when DeleteAttendanceCommand is executed.
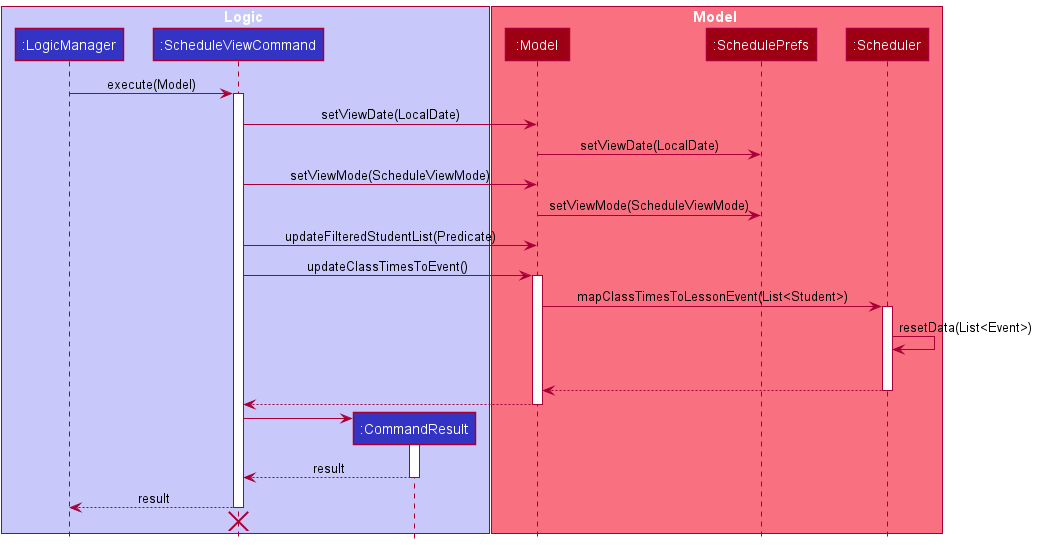
6.4 Schedule Command
This section describes the operations that ScheduleViewCommand performs.
- Upon successful parsing of the user input, the
ScheduleViewCommand#execute(Model)method is called. - The method
Model#setViewDate(LocalDate)is then called to set the viewing date of the user inSchedulePrefs - Similarly, the method
ModelsetViewMode(ScheduleViewMode)is called next to set the viewing mode (weekly/daily) of the user inSchedulePrefs. - After which, the method
updateFilteredStudentList(Predicate)is called to get all the students. ThePredicateargument will bePREDICATE_SHOW_ALL_STUDENTSwhich is a reusable final predicate variable. - Thereafter, the method
Model#updateClassTimesToEvent()will be called to translate all student’sClassTimetoLessonEvent - The
Schedulerthen calls the methodresetData(List<Event>)with the updatedLessonEventobjects. - The
CommandResultis then returned.
The following sequence diagram illustrates to execution of the ScheduleViewCommand:
The following activity diagram summarizes the flow of events when the ScheduleViewCommand is being executed:
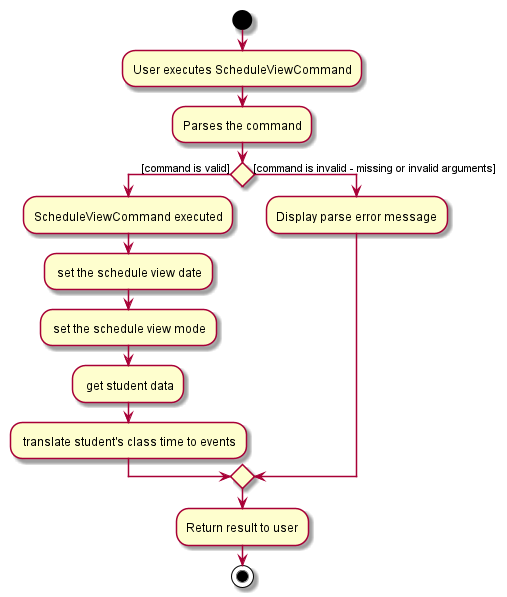
![]() Figure 43 and 44 illustrates the
Figure 43 and 44 illustrates the ScheduleCommand execution within the Logic and Model Component.
For the Ui component, a calendar using jfxtras-icalendarfx will be updated with the LessonEvent after the CommandResult is returned.
The 'LessonEvent is provided to the Ui by the LogicManager through the Model component.
The Model in turns gets the LessonEvent from the Scheduler which keeps a list of updated events.
The calendar with LessonEvent is then displayed to the user through the interface. This is assuming that no exception arises.
The following are the various design choices made regarding the feature and alternatives that were considered prior to implementation.
- Current Implementation:
- The current implementation creates
LessonEventfrom thestudentListand update to theUiwhenever theScheduleViewCommandis called.
- The current implementation creates
- Alternatives Considered:
- Creating a
Eventstorage component that storesLessonEventbased onStudent’sClassTime. This would violate the data integrity of theStudentwe currently have and introduce additional complexity in maintaining both data structures.
- Creating a
6.5 Notebook feature
This section describes the implementation of the notebook feature and the various commands relating to notebook.
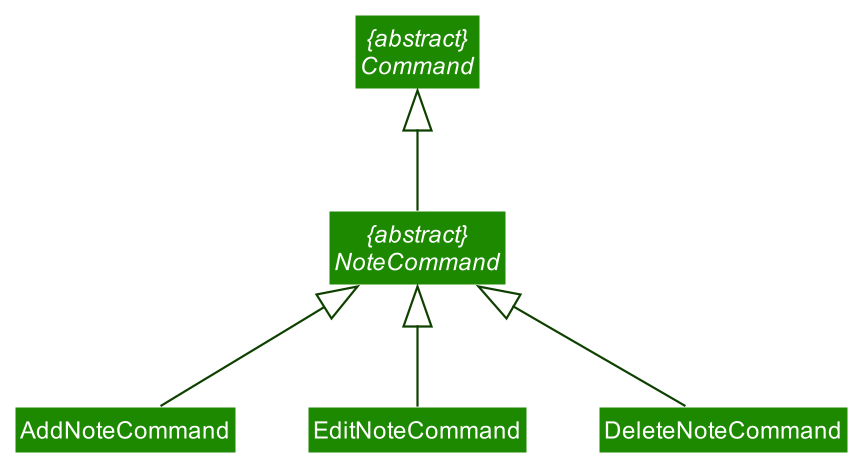
The notebook feature comprises three specific commands extending NoteCommand:
-
AddNoteCommand– Adds a note to the notebook. -
EditNoteCommand– Edits a note in the notebook. -
DeleteNoteCommand– Deletes a note from the notebook
The following class diagram shows how the various commands relate to each other. (refer to 5.3 Logic Component for higher-level details about the design)
6.5.1 Add note command
This section describes how AddNoteCommand is performed.
- Upon successful parsing of the user input,
AddNoteCommand#execute(Model model)is called which checks whether there is already a note with the same title inNotesListusingModel#hasNote(Note toAdd). - If a duplicate note is found, a
CommandExceptionis thrown, and the note will not be added. - Otherwise,
Model#addNote(Note toAdd)will be called, and the note will be added. - A
CommandResultwill be returned with the success message.
6.5.2 Edit note command
This section describes how EditNoteCommand is performed.
- Upon successful parsing of the user input,
EditNoteCommand#execute(Model model)is called. - During the execution,
Model#getNotebook()is called to retrieve the notebook in Reeve andReadOnlyNotebook#getNotesList()is called from the notebook to retrieve the list of notes. - The
Indexis checked to ensure that it is valid; if it is not, aCommandExceptionis thrown, and no note will be edited. - The note at
indexis retrieved, and a new note,editedNoteis created based on this note and theEditNoteDescriptorstored within theEditNoteCommand. -
editedNoteis checked to ensure that it is not the same as the original note retrieved. ACommandExceptionis thrown if it is the same note. -
Model#setNote(Note notetoEdit, Note editedNote)is called to editnoteToEdittoeditedNoteinmodel. - A
CommandResultwill be returned with the success message.
6.5.3 Delete note command
This section describes how DeleteNoteCommand is performed.
- Upon successful parsing of the user input,
DeleteNoteCommand#execute(Model model)is called. - During the execution,
Model#getNotebook()is called to retrieve theReadOnlyNotebookin Reeve andReadOnlyNotebook#getNotesList()is called to retrieve theList<Note>. - The
Indexis checked to ensure that it is valid; if it is not, aCommandExceptionis thrown, and no note will be deleted. - The
NoteatIndexis removed from the notebook usingModel#deleteNote(Note noteToDelete). - A
CommandResultwill be returned with the success message.
7. Documentation
Refer to the Documentation guide.
8. Logging
Refer to the Logging guide.
9. Testing
Refer to the Testing guide.
10. Configuration
Refer to the Configuration guide.
11. DevOps
Refer to the DevOps guide.
Appendix A: Product Scope
Target user profile:
- is a Singapore primary/secondary/junior college 1 to 1 private tutors
- has a need to manage a significant number of student contacts
- has a need to manage administrative details of students
- has a need to manage academic details of students
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: Helps tutors organise administrative and academic details of their students with ease and manage student needs better.
Appendix B: User Stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * |
private tutor ready to use Reeve | view a list of commands and how to use them | learn how the application works or in case I forgot how some of the commands work |
* * * |
private tutor ready to use Reeve | add my students’ details | store them and retrieve them whenever I need |
* * * |
private tutor | view my students’ preferred tutoring location | figure out how to get that location |
* * * |
private tutor | edit my students’ personal details | update outdated data |
* * * |
private tutor | view my student’s details | refer to them when needed |
* * * |
private tutor | add additional details to each student | add other miscellaneous details which can allow me to better cater to student needs |
* * * |
private tutor with many students | find a student’s record | retrieve students’ data with ease |
* * * |
private tutor | find students who have not paid their fees | remind students who have yet to pay me for my services |
* * * |
private tutor who is a long-term user | delete students’ data | remove irrelevant data of students who are no longer my tutees |
* * |
private tutor | record questions that my students raised | find the answers to them after the lesson |
* * |
private tutor | record solutions to the questions raised | use them as reference for answering future similar questions |
* * |
private tutor | delete questions I do not need anymore | focus on the questions I need to pay attention to |
* * |
private tutor | input my student’s school test scores | keep track of their progress |
* * |
private tutor | track my students’ attendance | keep track of students’ lesson records |
* * |
private tutor | input feedback to specific lessons | improve my capabilities as a tutor |
* * |
private tutor | keep track of notes | store small pieces of information in case I forget |
* * |
private tutor | view my tutoring schedule for a particular day | plan ahead of my lessons for that day |
* * |
private tutor | be able to view students in alphabetical order | look for students easily |
* * |
private tutor | be able to my view my students in lesson time order | know which students to prioritise when preparing lessons |
* * |
private tutor | be able to group my students by their year of study | look at questions and queries together for one cohort together |
* * |
private tutor | view my tutoring schedule for a week | plan for the week ahead |
* |
private tutor | view my students’ academic progress | know which students need more help |
* |
private tutor ready to use Reeve | view the type of student details that are displayed | focus on the details that I am currently concerned with |
* |
private tutor that is impatient | be able to get the command results in a reasonable time | save time |
* |
private tutor that is using Reeve for the first time | view Reeve with sample data | visualize how Reeve looks like when I use it |
Appendix C: Use Cases
For all use cases below, the System is Reeve and the Actor is the Tutor (User), unless specified otherwise.
Use cases also assume that whenever an invalid command is entered by the user, Reeve displays an error message.
UC01: Displaying help menu
MSS
- User enters a command to open help menu.
-
Reeve displays a success message and the help menu.
Use case ends.
UC02: Toggling displays between administrative and academic details of students
MSS
- User enters a command to toggle display students details.
-
Reeve displays a success message and the toggled display of students details.
Use case ends.
UC03: Exiting the application
MSS
- User enters a command to exit the application.
-
All processes of Reeve ends.
Use case ends.
UC04: Adding a student
MSS
- User enters a command to add a student with student details.
-
Reeve saves student data into the students list and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. User provides input with missing compulsory fields.
-
1a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes from step 1.
-
- 1b. User provides input with invalid format.
-
1b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes from step 1.
-
UC05: Listing all students
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
-
Reeve displays the students list with student details.
Use case ends.
UC06: Editing a student’s admin details
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve shows the list of students.
- User enters command to edit a specific student in the list and provides needed parameters.
-
Reeve updates the specified student with the input parameters and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty. Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with invalid index.
-
3a1. Reeve requests for input with valid index.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User provides input without any parameters.
-
3b1. Reeve requests for input with parameters.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3c. User provides input with invalid format.
-
3c1. Reeve requests for input with valid format.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC07: Deleting a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to delete a specific student in the list.
-
Reeve deletes the student and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. User provides input with invalid index.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC08: Searching for a student
MSS
- User enters a command to find all students that match the given search parameter (name, school, year).
-
Reeve displays all students matching the criteria.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. User provides input with invalid data into the search parameter.
-
1a1. Reeve displays erroneous field and expected format.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1b. User provides input without a search parameter.
-
1a1. Reeve displays a message indicating a search parameter was not provided.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1c. No students match the given criteria.
-
1c1. Reeve displays a message indicating no match found.
Use case ends.
-
UC09: Clearing all student records
MSS
- User enters a command to clear the students list.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
UC10: Sorting the list of students
MSS
- User enters a command to sort students by a given method (name, class time, year).
- Reeve sorts the list of students by the method.
-
Reeve displays the student list in the new order
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. User provides input with invalid format.
-
1a1. Reeve displays expected format.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1b. User provides input without a search parameter.
-
1a1. Reeve displays a message indicating a search parameter was not provided.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1c. User provides invalid means to sort students.
-
1c1. Reeve displays a message indicating that sorting means in valid and valid sorting means.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
UC11: Adding an additional detail to a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to add a detail to a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the newly added detail.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student index.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User inputs a detail in an invalid format.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC12: Editing an additional detail in a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to edit a detail from a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the edited detail.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User provides input with an invalid detail.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC13: Deleting an additional detail from a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to delete a detail from a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the removed detail.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User provides input with an invalid detail.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC14: Adding a question to a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to add an unresolved question to a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the newly added question.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student index.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User inputs a question in an invalid format.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC15: Resolving a question from a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to resolve a question from a specific student in the list with a solution.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the updated question.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User provides input with an invalid question.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3c. User inputs the solution in an invalid format.
-
3c1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3d. User specifies a question that has already been solved.
-
3d1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC16: Deleting a question from a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to delete a question from a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the removed question.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User provides input with an invalid question.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC17: Finding all students with overdue tuition fees
MSS
- User enter command to filter all students by those who have not paid their fees in the past month.
-
Reeve displays all students that match the above criteria.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
1b. All students have paid their fees in the past month.
-
1b1. Reeve displays an empty list.
Use case ends.
-
UC18: Adding an exam record to a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to add an exam record to a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the newly added exam record.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student index.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User inputs an exam record in an invalid format.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC19: Deleting an exam record from a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to delete a specific exam record from a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the removed question.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User provides input with an invalid exam record.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC20: Displaying exam statistics of a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to view the exam statistics on a specific student.
-
Reeve displays a success message and the exam statistics.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. User provides input with an invalid student.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC21: View class schedule.
MSS
- User enters command to view schedule.
-
Reeve shows the schedule of the user’s classes.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. User enters command in an incorrect format. 1a1. Reeve displays error message. 1a2. User corrects command input.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
1b. There are no student in Reeve. 1b1. Schedule is shown with no classes.
Use case ends.
UC22: Adding an attendance record to a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to add an attendance record to a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the newly added attendance record.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student index.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User inputs attendance with an invalid format.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC23: Deleting an attendance record from a student
MSS
- User enters a command to list students.
- Reeve displays a list of students.
- User enters a command to delete an attendance record from a specific student in the list.
- Reeve updates the specified student in the list with the removed attendance record.
-
Reeve displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. User provides input with an invalid student.
-
3a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 3b. User provides input with an invalid attendance record.
-
3b1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
UC24: Adding a note to the notebook
MSS
- User enters a command to add a note to the notebook.
- Reeve saves the note into the notebook and displays a success message
- 1a. User provides input with missing fields.
-
1a1. Reeve displays an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1b. User provides invalid input.
-
1b1. Reeve displays an error message and input constraints.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
UC25: Editing a note in the notebook
MSS
- User enters command to edit a specific note in the notebook and provides needed parameters.
-
Reeve updates the specified note with the input parameters and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. User provides input with invalid index.
-
1a1. Reeve displays an error message and requests for input with valid index.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1b. User provides input without any parameters.
-
1b1. Reeve requests for input with parameters.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1c. User provides input with invalid format.
-
1c1. Reeve requests for input with valid format.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
UC26: Editing a note in the notebook
MSS
- User enters command to edit a specific note in the notebook and provides needed parameters.
-
Reeve updates the specified note with the input parameters and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. User provides input with invalid index.
-
1a1. Reeve displays an error message and requests for input with valid index.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1b. User provides input without any parameters.
-
1b1. Reeve requests for input with parameters.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1c. User provides input with invalid format.
-
1c1. Reeve requests for input with valid format.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Appendix D: Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - The response to any use action should become visible within 5 seconds.
- The program should be able to handle at least 100 students (in practice, our target audience should not require as high a capacity, but this is a buffer to ensure it will not fail).
- The graphical user interface should be easy to use for non-IT savvy users.
- The program should be able to run even without internet connection.
Appendix E: Glossary
The following table provides the definitions of the various terms used in this Developer Guide.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Mainstream OS | Refers to Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X |
| Private contact detail | A contact detail that is not meant to be shared with others |
Appendix F: Instructions for Manual Testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
F.1 Launching Reeve
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample students. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
F.2 General Features
-
Opening help window.
-
Test case:
helpwhen no help window is opened.
Expected: Expected: Help window opens. -
Test case:
helpwhen help window is already opened.
Expected: Expected: Brings up already opened help window.
-
-
Toggling between student details.
-
Test case:
togglewhen students display administrative details.
Expected: Expected: Students switch to display academic details. -
Test case:
togglewhen students display academic details.
Expected: Expected: Students switch to display administrative details.
-
-
Exiting Reeve.
- Test case:
exit.
Expected: Reeve shuts down.
- Test case:
F.3 Student Administrative Features
-
Adding a student with administrative details to the students list.
-
Test case:
add n/Brendan Tan p/93211234 s/Commonwealth Secondary School y/pri 6 v/Blk 33 West Coast Rd #21-214 t/5 1430-1630 f/25 d/10/10/2020
Expected: Expected: Student Brendan Tan has been added to the students list. -
Test case:
add n/Brendan Tan p/93211234 s/Commonwealth Secondary School v/Blk 33 West Coast Rd #21-214 t/5 1430-1630 f/25 d/50/50/2020 a/Likes Algebra
Expected: Expected: No student is added as due to invalid payment date. Error details displayed in the result display. -
Test case:
add n/Brendan Tan p/93211234 s/Commonwealth Secondary School v/Blk 33 West Coast Rd #21-214 t/15 1430-1630 f/25 d/10/10/2020 a/Likes Algebra
Expected: Expected: No student is added as due to invalid class time. Error details displayed in the result display.
-
-
Deleting a student while all students are being shown.
-
Prerequisites: At least one student in the students list.
-
Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First student is deleted from the students list. Details of the deleted student shown in the result display. -
Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No student is deleted. Error details shown in the result display. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Finding students with overdue fees (i.e last payment date is more than one month ago) while all students are shown.
-
Prerequisite: Set at least one student’s last payment date to within one month of the current date with
editcommand. Multiple students in the list. -
Test case:
overdue
Expected: All students except those whose payment date is within one month from the current date are listed. The number of students found is displayed.
-
-
Finding students with overdue fees while some students are hidden.
-
Prerequisite: Hide some students with overdue fees with
findcommand. -
Test case:
overdue
Expected: All students except those whose payment date is within one month from the current date are displayed again. The number of students found is displayed.
-
-
Viewing schedule of classes
-
Prerequisites: There are students stored in Reeve currently with non-overlapping class times.
-
Test case:
schedule m/weekly d/02/11/2020Expected: Shows the schedule of classes in the whole week of 02/11/2020. -
Test case:
schedule m/daily d/02/11/2020Expected: Shows the schedule of classes in the day of 02/11/2020. -
Test case:
schedule m/dAiLy d/02/11/2020Expected: Shows the schedule successfully as the case letters of the view mode does not matter. -
Test case:
schedule m/day d/02/11/2020Expected: Displays error message indicating invalid view mode. -
Test case:
schedule m/weekly d/02-11-2020Expected: Displays error message indicating invalid date format.
-
-
Finding a student while all students are being shown with several matching students
-
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Two students in the list. One student has name Samuel and has school yishun secondary. Another student has name Sam and has school yishun sec school. -
Test case:
find n/samuel
Expected: Only the student with name Samuel and school yishun secondary shows up in the list. -
Test case:
find n/sam
Expected: Only the student with name Sam and school yishun sec school showsinp on the list. -
Test case:
find s/yishun sec
Expected: Both students show up in the list. -
Incorrect find commands to try:
find,find samuel,find yishun secExpected: No changes show up on the list. Error details shown in the status message.
-
-
Adding details to a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. Multiple students present. -
Test case:
detail add 1 t/DETAIL_TEXTExpected: New detail that matches your inputDETAIL_TEXTadded to first student. -
Test case:
detail add 0 t/DETAIL_TEXTExpected: No detail added. Error details shown in status message. List stays the same. -
Test case:
detail add 1 t/Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
detail add t/DETAIL_TEXTExpected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Editing details for a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. Multiple students present. Student to be edited has at least one detail. -
Test case:
detail edit 1 i/1 t/DETAIL_TEXTExpected: New detail that matches your inputDETAIL_TEXTreplaces the first detail for first student. -
Test case:
detail edit 0 i/1 t/DETAIL_TEXTExpected: No detail edited. Error details shown in status message. List stays the same. -
Test case:
detail edit 1 i/1 t/Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
detail edit 1 i/ t/DETAIL_TEXTExpected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
detail edit i/1 t/DETAIL_TEXTExpected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Deleting details from a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. Multiple students present. Student to be edited has at least one detail. -
Test case:
detail delete 1 i/1Expected: First detail in first student is deleted. -
Test case:
detail delete 0 i/1Expected: No detail deleted. Error details shown in status message. -
Test case:
detail delete i/1Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
detail deleteExpected: Similar to previous.
-
F.4 Student Academic Features
-
Adding an exam record to a student.
-
Prerequisites: At least one student in the students list.
-
Test case:
exam add 1 n/Mid Year 2020 d/08/12/2020 s/40/60
Expected: Mid Year 2020 exam record is added to the exams list of the first student in the displayed students list. -
Test case:
exam add 1 n/Mid Year 2020 d/08/12/2020 s/50/10
Expected: No exam record is added due to invalid score as numerator is larger than denominator. -
Test case:
exam add 1 n/Mid Year 2020 d/30/30/2020 s/50/100
Expected: No exam record is added due to invalid exam date.
-
-
Deleting an exam record from a student.
-
Prerequisites: At least one student in the students list. At least one exam record in the student’s exams list.
-
Test case:
exam delete 1 i/1
Expected: First exam record of the exam list of the first student in the displayed students list is deleted. Details of deleted exam record shown in the result display. -
Test case:
exam delete 1 i/0
Expected: No exam is deleted due to invalid exam index. Error details shown in the result display.
-
-
Displaying exam statistics of a student
-
Prerequisites: At least one student in the students list.
-
Test case:
exam stats 1
Expected: Opens the exam statistics window of the first student in the displayed students list.
-
-
Adding attendance to a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. Multiple students present. -
Test case:
attendance add 1 d/12/02/2020 a/presentExpected: New attendance that matches the input date and status is added to the first student. -
Test case:
attendance add 1 d/12/02/2020 a/present f/attentiveExpected: New attendance that matches the input date, status and feedback is added to the first student. -
Test case:
attendance add 1 d/12/02/2020 a/preExpected: No attendance added. Error details shown in status message. List stays the same. -
Test case:
attendance add 1 d/12/02 a/presentExpected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Deleting attendance record from a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. Multiple students present. Student to be edited has at least one attendance record. -
Test case:
attendance delete 1 d/12/02/2020Expected: Attendance record that has the input date in the first student is deleted. -
Test case:
attendance delete 1 d/12/02Expected: No attendance deleted. Error details shown in status message. -
Test case:
attendance delete d/12/02/2020Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Adding questions to a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. View academic data withtogglecommand. Multiple students present. -
Test case:
question add 1 t/RANDOM_QUESTIONExpected: New unresolved (cross symbol) question whose description matches your input added to first student. -
Test case:
question add 0 t/RANDOM_QUESTIONExpected: No question added. Error details shown in status message. List stays the same. -
Test case:
question add 1 t/Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
question add 1 t/SAME_QUESTION_IN_TEST_CASE_2Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Resolving questions from a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. View academic data withtogglecommand. First student on the list must have at least one unresolved question. -
Test case:
question solve 1 i/UNSOLVED_QUESTION_INDEX t/Expected: No question resolved. Error details shown in status message. -
Test case:
question solve 1 i/UNSOLVED_QUESTION_INDEX t/RANDOM_SOLUTIONExpected: Status of question atUNSOLVED_QUESTION_INDEXchanged to a tick,RANDOM_SOLUTIONadded next to the question text in square brackets ([]). Details of the question resolved and student’s name included in status message. -
Test case:
question solve 0 i/1 t/RANDOM_SOLUTIONExpected: No question resolved. Error details shown in status message. -
Test case:
question solve 1 i/0 t/RANDOM_SOLUTIONExpected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
question solve 1 i/INDEX_OF_QUESTION_SOLVED_IN_TEST_CASE_2 t/RANDOM_SOLUTIONExpected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Deleting questions from a student.
-
Prerequisite: List all students using
listcommand. View academic data withtogglecommand. First student on the list must have at least one question. -
Test case:
question delete 0 i/1Expected: No question deleted. Error details shown in status message. -
Test case:
question delete 1 i/0Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
question delete 1 i/QUESTION_INDEXExpected: Question atQUESTION_INDEXis removed. Details of deleted question included in status message.
-
F.5 Notebook Feature
-
Adding a note to the notebook.
-
Test case:
note add t/things to do d/mark practice papers
Expected: Note with title things to do is added and details shown in the results display. -
Test case:
note add t/things to finish by tomorrow d/mark practice papers
Expected: No note is added due to a title that is too long. Error details shown in the results display.
-
-
Deleting a note.
-
Prerequisites: At least one note in the notebook.
-
Test case:
note delete 1
Expected: First note is deleted from the notebook. Details of the deleted note shown in the result display. -
Test case:
note delete 0
Expected: No note is deleted. Error details shown in the result display.
-
F.6 Saving Data
-
Dealing with missing data files
-
Test case:
data/addressbook.jsonmissing or deleted
Expected: Reeve initialises with sample student data, notebook data is intact. -
Test case:
data/notebook.jsonmissing or deleted
Expected: Reeve initialises with sample notebook data, student data is intact.
-
-
Dealing with corrupted data files (Student data)
-
Prerequisite: Ensure
data/addressbook.jsonis present. Modify the data usingeditordeleteto createdata/addressbook.jsonif absent. -
Test case: delete a random field from a random student in
addressbook.json
Expected: Reeve initialises with an empty student list. -
Test case: duplicate a student’s record again in
addressbook.json
Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case: invalid data in
addressbook.json(e.g add special characters to the “name” field)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Dealing with corrupted data files (Notebook data)
-
Prerequisite: Ensure
data/notebook.jsonis present. Modify the data using note commands to createdata/notebook.jsonif absent. -
Test case: “description” field has more than 80 characters
Expected: Reeve initialises with an empty notebook. -
Test case: “title” field has more than 15 characters
Expected: Reeve initialises with an empty notebook. -
Test case: duplicate note in
notebook.json
Expected: Similar to previous.
-